Page 74 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part2
P. 74
7.2 Molecular Mechanisms That Alter DNA Sequence 233
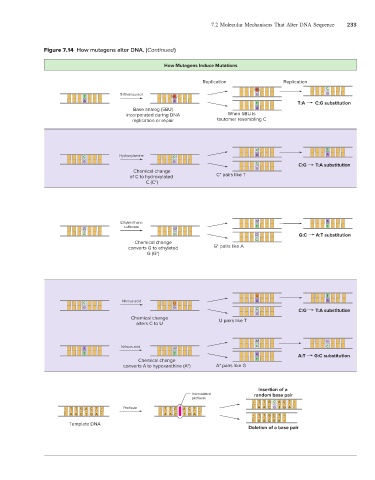
Figure 7.14 How mutagens alter DNA. (Continued )
How Mutagens Induce Mutations
Replication Replication
5BU C
5-Bromouracil G G
T 5BU
A A
T T:A C:G substitution
Base analog (5BU) A
incorporated during DNA When 5BU is
replication or repair tautomer resembling C
C* T
C Hydroxylamine C* A A
G G C C:G T:A substitution
G
Chemical change
of C to hydroxylated C* pairs like T
C (C*)
Ethylmethane G* A
sulfonate T T
G G*
C C G G:C A:T substitution
C
Chemical change
converts G to ethylated G* pairs like A
G (G*)
U T
C Nitrous acid U A A
G G C
G C:G T:A substitution
Chemical change U pairs like T
alters C to U
A* G
Nitrous acid C C
A A*
T T A A:T G:C substitution
Chemical change T
converts A to hypoxanthine (A*) A* pairs like G
Insertion of a
Intercalated random base pair
proflavin
T T G C A C T
T T G A C T Proflavin T T G A C T A A C G T G A
A A C T G A A A C T G A T T G C T
A A C G A
Template DNA
Deletion of a base pair