Page 78 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part2
P. 78
7.3 DNA Repair Mechanisms 237
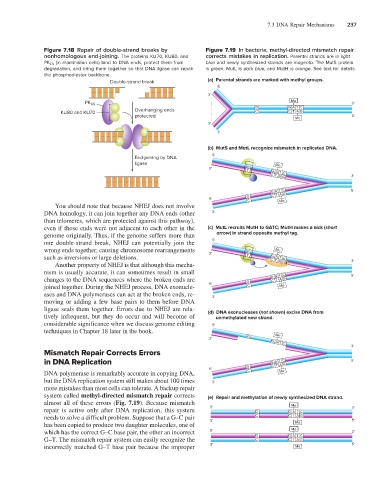
Figure 7.18 Repair of double-strand breaks by Figure 7.19 In bacteria, methyl-directed mismatch repair
nonhomologous end-joining. The proteins KU70, KU80, and corrects mistakes in replication. Parental strands are in light
PK CS (in mammalian cells) bind to DNA ends, protect them from blue and newly synthesized strands are magenta. The MutS protein
degradation, and bring them together so that DNA ligase can repair is green, MutL is dark blue, and MutH is orange. See text for details.
the phosphodiester backbone.
Double-strand break (a) Parental strands are marked with methyl groups.
5'
3'
PK cs MeMe 3'
G A T
Overhanging ends G G C C G A T CC GG
AA
C
C TT
KU80 and KU70
protected 5'
MeMe
5'
3'
(b) MutS and MutL recognize mismatch in replicated DNA.
End-joining by DNA 5'
ligase Me
3' G
T
G A T C
C T A G 3'
G A T C G 5'
G C T A
5' C Me
You should note that because NHEJ does not involve
DNA homology, it can join together any DNA ends (other 3'
than telomeres, which are protected against this pathway),
even if those ends were not adjacent to each other in the (c) MutL recruits MutH to GATC; MutH makes a nick (short
genome originally. Thus, if the genome suffers more than arrow) in strand opposite methyl tag.
one double-strand break, NHEJ can potentially join the 5'
wrong ends together, causing chromosome rearrangements 3' G Me
such as inversions or large deletions. T C T 3'
G A T C
Another property of NHEJ is that although this mecha- A G
nism is usually accurate, it can sometimes result in small 5'
changes to the DNA sequences where the broken ends are G G A T C G
A
C T
joined together. During the NHEJ process, DNA exonucle- 5' C Me
ases and DNA polymerases can act at the broken ends, re- 3'
moving or adding a few base pairs to them before DNA
ligase seals them together. Errors due to NHEJ are rela- (d) DNA exonucleases (not shown) excise DNA from
tively infrequent, but they do occur and will become of unmethylated new strand.
considerable significance when we discuss genome editing 5'
techniques in Chapter 18 later in the book.
3' G Me
G A T C
3'
Mismatch Repair Corrects Errors
in DNA Replication G A T C G 5'
A
5' G C C T
DNA polymerase is remarkably accurate in copying DNA, Me
but the DNA replication system still makes about 100 times 3'
more mistakes than most cells can tolerate. A backup repair
system called methyl-directed mismatch repair corrects (e) Repair and methylation of newly synthesized DNA strand.
almost all of these errors (Fig. 7.19). Because mismatch Me
repair is active only after DNA replication, this system 5' G G A T C 3'
needs to solve a difficult problem. Suppose that a G–C pair 3' C C T A G 5'
has been copied to produce two daughter molecules, one of Me
Me
which has the correct G–C base pair, the other an incorrect 5' G G A T C 3'
G–T. The mismatch repair system can easily recognize the C C T A G
incorrectly matched G–T base pair because the improper 3' Me 5'