Page 75 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part2
P. 75
234 Chapter 7 Anatomy and Function of a Gene: Dissection Through Mutation
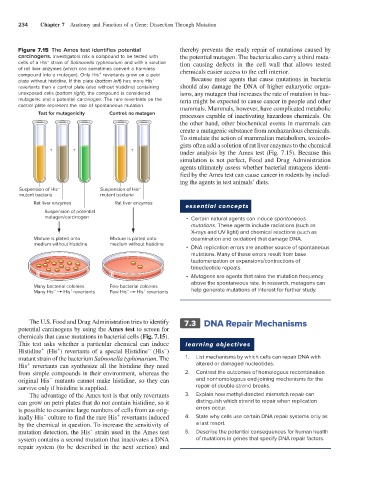
Figure 7.15 The Ames test identifies potential thereby prevents the ready repair of mutations caused by
carcinogens. Investigators mix a compound to be tested with the potential mutagen. The bacteria also carry a third muta-
−
cells of a His strain of Salmonella typhimurium and with a solution tion causing defects in the cell wall that allows tested
of rat liver enzymes (which can sometimes convert a harmless chemicals easier access to the cell interior.
+
compound into a mutagen). Only His revertants grow on a petri
+
plate without histidine. If this plate (bottom left) has more His Because most agents that cause mutations in bacteria
revertants than a control plate (also without histidine) containing should also damage the DNA of higher eukaryotic organ-
unexposed cells (bottom right), the compound is considered isms, any mutagen that increases the rate of mutation in bac-
mutagenic and a potential carcinogen. The rare revertants on the teria might be expected to cause cancer in people and other
control plate represent the rate of spontaneous mutation. mammals. Mammals, however, have complicated metabolic
Test for mutagenicity Control: no mutagen processes capable of inactivating hazardous chemicals. On
the other hand, other biochemical events in mammals can
create a mutagenic substance from nonhazardous chemicals.
To simulate the action of mammalian metabolism, toxicolo-
gists often add a solution of rat liver enzymes to the chemical
+ + + under analysis by the Ames test (Fig. 7.15). Because this
simulation is not perfect, Food and Drug Administration
agents ultimately assess whether bacterial mutagens identi-
fied by the Ames test can cause cancer in rodents by includ-
ing the agents in test animals’ diets.
Suspension of His – Suspension of His –
mutant bacteria mutant bacteria
Rat liver enzymes Rat liver enzymes
essential concepts
Suspension of potential
mutagen/carcinogen • Certain natural agents can induce spontaneous
mutations. These agents include radiations (such as
X-rays and UV light) and chemical reactions (such as
Mixture is plated onto Mixture is plated onto deamination and oxidation) that damage DNA.
medium without histidine medium without histidine
• DNA replication errors are another source of spontaneous
mutations. Many of these errors result from base
tautomerization or expansions/contractions of
trinucleotide repeats.
• Mutagens are agents that raise the mutation frequency
above the spontaneous rate. In research, mutagens can
Many bacterial colonies Few bacterial colonies
–
–
+
+
Many His His revertants Few His His revertants help generate mutations of interest for further study.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration tries to identify 7.3 DNA Repair Mechanisms
potential carcinogens by using the Ames test to screen for
chemicals that cause mutations in bacterial cells (Fig. 7.15).
This test asks whether a particular chemical can induce learning objectives
+
−
+
−
Histidine (His ) revertants of a special Histidine (His )
mutant strain of the bacterium Salmonella typhimurium. The 1. List mechanisms by which cells can repair DNA with
+
His revertants can synthesize all the histidine they need altered or damaged nucleotides.
from simple compounds in their environment, whereas the 2. Contrast the outcomes of homologous recombination
−
original His mutants cannot make histidine, so they can and nonhomologous end-joining mechanisms for the
survive only if histidine is supplied. repair of double-strand breaks.
The advantage of the Ames test is that only revertants 3. Explain how methyl-directed mismatch repair can
can grow on petri plates that do not contain histidine, so it distinguish which strand to repair when replication
is possible to examine large numbers of cells from an orig- errors occur.
−
+
inally His culture to find the rare His revertants induced 4. State why cells use certain DNA repair systems only as
by the chemical in question. To increase the sensitivity of a last resort.
−
mutation detection, the His strain used in the Ames test 5. Describe the potential consequences for human health
system contains a second mutation that inactivates a DNA of mutations in genes that specify DNA repair factors.
repair system (to be described in the next section) and