Page 73 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part2
P. 73
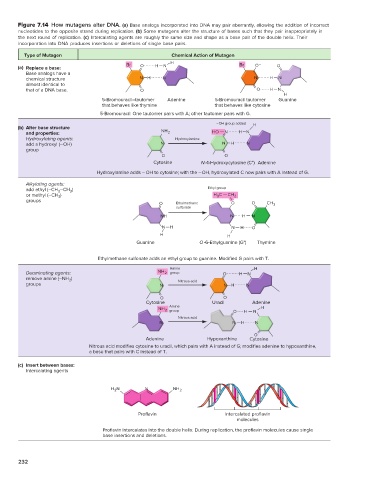
Figure 7.14 How mutagens alter DNA. (a) Base analogs incorporated into DNA may pair aberrantly, allowing the addition of incorrect
nucleotides to the opposite strand during replication. (b) Some mutagens alter the structure of bases such that they pair inappropriately in
the next round of replication. (c) Intercalating agents are roughly the same size and shape as a base pair of the double helix. Their
incorporation into DNA produces insertions or deletions of single base pairs.
Type of Mutagen Chemical Action of Mutagen
Br H Br O –
(a) Replace a base: O H N O
Base analogs have a
chemical structure N H N N H N
almost identical to
that of a DNA base. O O H N
H
5-Bromouracil–tautomer Adenine 5-Bromouracil tautomer Guanine
that behaves like thymine that behaves like cytosine
5-Bromouracil: One tautomer pairs with A; other tautomer pairs with G.
–OH group added H
(b) Alter base structure
and properties: NH 2 HO N H N
Hydroxylating agents: Hydroxylamine
add a hydroxyl (–OH) N N H N
group
O O
Cytosine N-4-Hydroxycytosine (C*) Adenine
Hydroxylamine adds – OH to cytosine; with the –OH, hydroxylated C now pairs with A instead of G.
Alkylating agents: Ethyl group
3
add ethyl (–CH 2 –CH )
or methyl (–CH ) H C CH 2
3
3
groups
O Ethylmethane O O CH 3
sulfonate
NH N H N
N H N H O
H H
Guanine O-6-Ethylguanine (G*) Thymine
Ethylmethane sulfonate adds an ethyl group to guanine. Modified G pairs with T.
Amine H
Deaminating agents: NH 2 group O H N
remove amine (–NH 2 ) Nitrous acid
groups N N H N
O O
Cytosine Uracil Adenine
NH 2 Amine O H N H
group
Nitrous acid
N N H N
O
Adenine Hypoxanthine Cytosine
Nitrous acid modifies cytosine to uracil, which pairs with A instead of G; modifies adenine to hypoxanthine,
a base that pairs with C instead of T.
(c) Insert between bases:
Intercalating agents
H N N NH 2
2
Proflavin Intercalated proflavin
molecules
Proflavin intercalates into the double helix. During replication, the proflavin molecules cause single
base insertions and deletions.
232