Page 69 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part2
P. 69
228 Chapter 7 Anatomy and Function of a Gene: Dissection Through Mutation
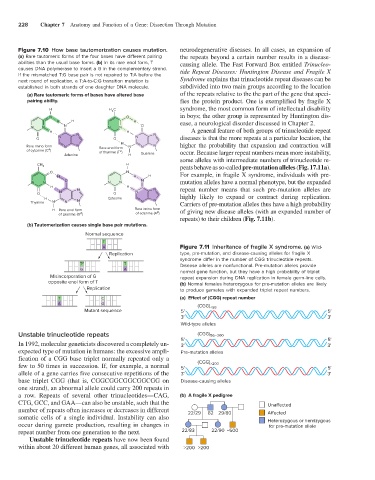
Figure 7.10 How base tautomerization causes mutation. neurodegenerative diseases. In all cases, an expansion of
(a) Rare tautomeric forms of the four bases have different pairing the repeats beyond a certain number results in a disease-
abilities than the usual base forms. (b) In its rare enol form, T causing allele. The Fast Forward Box entitled Trinucleo-
causes DNA polymerase to insert a G in the complementary strand. tide Repeat Diseases: Huntington Disease and Fragile X
If the mismatched T:G base pair is not repaired to T:A before the
next round of replication, a T:A-to-C:G transition mutation is Syndrome explains that trinucleotide repeat diseases can be
established in both strands of one daughter DNA molecule. subdivided into two main groups according to the location
(a) Rare tautomeric forms of bases have altered base of the repeats relative to the the part of the gene that speci-
pairing ability. fies the protein product. One is exemplified by fragile X
H H 3 C syndrome, the most common form of intellectual disability
N O in boys; the other group is represented by Huntington dis-
H H H ease, a neurological disorder discussed in Chapter 2.
N N N N N O
H N H N A general feature of both groups of trinucleotide repeat
O N O N diseases is that the more repeats at a particular location, the
H
Rare imino form N N Rare enol form N N N higher the probability that expansion and contraction will
of cytosine (C ) # of thymine (T ) # occur. Because larger repeat numbers mean more instability,
Adenine H Guanine
some alleles with intermediate numbers of trinucleotide re-
H
peats behave as so-called pre-mutation alleles (Fig. 17.11a).
CH 3
O N For example, in fragile X syndrome, individuals with pre-
H H H
N N O N N N mutation alleles have a normal phenotype, but the expanded
H N H N repeat number means that such pre-mutation alleles are
O N O N highly likely to expand or contract during replication.
H Cytosine N
Thymine N N N N Carriers of pre-mutation alleles thus have a high probability
H Rare enol form Rare imino form of giving new disease alleles (with an expanded number of
#
of guanine (G ) # of adenine (A )
repeats) to their children (Fig. 7.11b).
(b) Tautomerization causes single base pair mutations.
Normal sequence
T
A Figure 7.11 Inheritance of fragile X syndrome. (a) Wild-
Replication type, pre-mutation, and disease-causing alleles for fragile X
syndrome differ in the number of CGG trinucleotide repeats.
T # T Disease alleles are nonfunctional. Pre-mutation alleles provide
G A normal gene function, but they have a high probability of triplet
Misincorporation of G repeat expansion during DNA replication in female germ-line cells.
opposite enol form of T (b) Normal females heterozygous for pre-mutation alleles are likely
Replication to produce gametes with expanded triplet repeat numbers.
T C (a) E ect of (CGG) repeat number
A G
(CGG) <56
Mutant sequence 5' 5'
3' 3'
Wild-type alleles
Unstable trinucleotide repeats (CGG) 56–200
5' 5'
In 1992, molecular geneticists discovered a completely un- 3' 3'
expected type of mutation in humans: the excessive ampli- Pre-mutation alleles
fication of a CGG base triplet normally repeated only a
few to 50 times in succession. If, for example, a normal 5' (CGG) >200 5'
allele of a gene carries five consecutive repetitions of the 3' 3'
base triplet CGG (that is, CGGCGGCGGCGGCGG on Disease-causing alleles
one strand), an abnormal allele could carry 200 repeats in
a row. Repeats of several other trinucleotides—CAG, (b) A fragile X pedigree
CTG, GCC, and GAA—can also be unstable, such that the Una ected
number of repeats often increases or decreases in different 22/29 82 29/80 A ected
somatic cells of a single individual. Instability can also Heterozygous or hemizygous
occur during gamete production, resulting in changes in for pre-mutation allele
repeat number from one generation to the next. 22/83 22/90 ~ 500
Unstable trinucleotide repeats have now been found
within about 20 different human genes, all associated with >200 >200