Page 67 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part2
P. 67
226 Chapter 7 Anatomy and Function of a Gene: Dissection Through Mutation
section of this chapter will discuss various biochemical path- backbone occurs 1000 times an hour in every human
ways that biological systems have evolved to minimize the cell. This kind of DNA alteration is called depurination
mutagenic consequences of these DNA alterations. (Fig. 7.8a). Because the resulting apurinic site cannot
specify a complementary base, the DNA replication pro-
cess introduces a random base opposite the apurinic site,
Natural Processes Cause Spontaneous causing a mutation in the newly synthesized complemen-
Mutations Through DNA Damage tary strand three-quarters of the time.
Another naturally occurring process that may mod-
Chemical and physical assaults on DNA are quite frequent. ify DNA’s information content is deamination: the re-
Geneticists estimate, for example, that the hydrolysis of moval of an amino (–NH 2 ) group. Deamination can
a purine base, A or G, from the deoxyribose-phosphate change cytosine (C) to uracil (U), the nitrogenous base
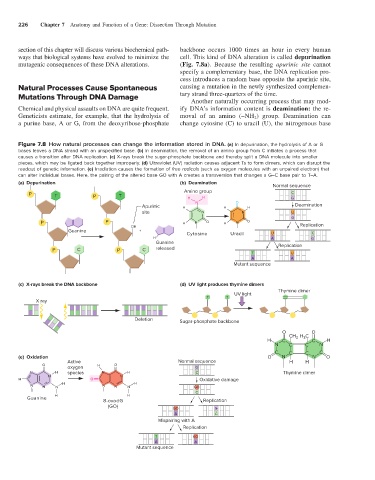
Figure 7.8 How natural processes can change the information stored in DNA. (a) In depurination, the hydrolysis of A or G
bases leaves a DNA strand with an unspecified base. (b) In deamination, the removal of an amino group from C initiates a process that
causes a transition after DNA replication. (c) X-rays break the sugar-phosphate backbone and thereby split a DNA molecule into smaller
pieces, which may be ligated back together improperly. (d) Ultraviolet (UV) radiation causes adjacent Ts to form dimers, which can disrupt the
readout of genetic information. (e) Irradiation causes the formation of free radicals (such as oxygen molecules with an unpaired electron) that
can alter individual bases. Here, the pairing of the altered base GO with A creates a transversion that changes a G–C base pair to T–A.
(a) Depurination (b) Deamination
Normal sequence
Amino group C
P T P T H H G
N O
Apurinic H H H Deamination
site N N U
G
P P H N O H N O
OH Replication
Guanine + Cytosine Uracil U C
H A G
Guanine Replication
P C P C released
T U
A A
Mutant sequence
(c) X-rays break the DNA backbone (d) UV light produces thymine dimers
Thymine dimer
UV light
T T
X ray
Deletion Sugar-phosphate backbone
O O
CH 3 H C
3
H C C H
N C C N
C C C C
(e) Oxidation O N N O
Active Normal sequence H H
O H O
oxygen G
N H species N H C Thymine dimer
N N
H O Oxidative damage
H H
N N N N N N GO
C
H H
Guanine
8-oxodG Replication
(GO)
GO G
A C
Mispairing with A
Replication
T GO
A A
Mutant sequence