Page 29 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part2
P. 29
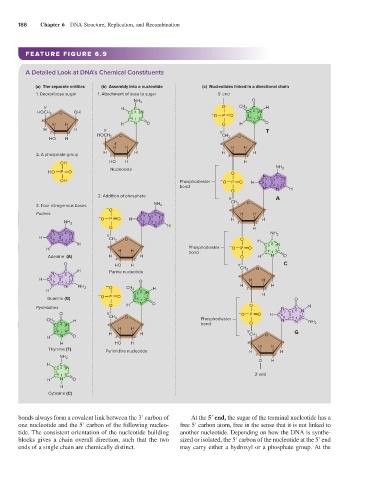
188 Chapter 6 DNA Structure, Replication, and Recombination
FEATURE FIGURE 6.9
A Detailed Look at DNA’s Chemical Constituents
(a) The separate entities (b) Assembly into a nucleotide (c) Nucleotides linked in a directional chain
1. Deoxyribose sugar 1. Attachment of base to sugar 5' end
O
NH 2
5' H C O CH 3 C H
HOCH 2 O OH C5 4 3 N – O P O C5 4 3 2 N
4' 1' C 6 1 2 C C 6 N 1 C O
H H H N O O H
H H 5' T
3' 2' 5'
HOCH 2 O CH 2 O
HO H
4' 1' 4' 1'
H H H H
H H H H
2. A phosphate group 3' 2' 3' 2'
OH HO H H
Nucleoside NH 2
HO P O O
N C 6 N
OH Phosphodiester – O P O H C 8 7 C 5 1
bond N 9 C 4 3 2 C
O N H
2. Addition of phosphate
5' A
CH 2 O
3. Four nitrogenous bases NH 2
– O 4' 1'
Purines N C 6 N H H
– O P O H C 8 7 C 5 1 H H
NH 2 N 9 C 4 3 2 C 3' 2'
O N H H
N 7 C 6 N NH 2
H C 8 9 C 5 4 2 1 C 5' CH 2 O O
N C N 3 H H C5 C 4 3 N
H 4' H H 1' Phosphodiester – O P O C 6 1 2 C
bond
Adenine (A) H H O H N O
3' 2'
O HO H 5' O C
N C 6 N H Purine nucleotide CH 2 1'
H C 8 9 7 C 5 4 2 1 O 4' H H
N C N 3 C NH 2 – H H
H O CH 3 C5 C 4 3 N H 3' 2'
– O P O H
Guanine (G) C 6 1 2 C O
O H N O O
Pyrimidines N C 6 N H
O 5' – O P O H C 8 7 C 5 1 2
CH 2 O Phosphodiester 9 C 4 3 C
CH 3 C H O N N NH 2
C5 4 3 N 4' H H 1' bond
C 6 1 2 C H H 5' O G
H N O 3' 2' CH 2
H HO H 4' 1'
Thymine (T) Pyrimidine nucleotide H H H H
3' 2'
NH 2
O H
H C
C5 4 3 N
C 6 1 2 C 3' end
H N O
H
Cytosine (C)
bonds always form a covalent link between the 3′ carbon of At the 5′ end, the sugar of the terminal nucleotide has a
one nucleotide and the 5′ carbon of the following nucleo- free 5′ carbon atom, free in the sense that it is not linked to
tide. The consistent orientation of the nucleotide building another nucleotide. Depending on how the DNA is synthe-
blocks gives a chain overall direction, such that the two sized or isolated, the 5′ carbon of the nucleotide at the 5′ end
ends of a single chain are chemically distinct. may carry either a hydroxyl or a phosphate group. At the