Page 27 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part2
P. 27
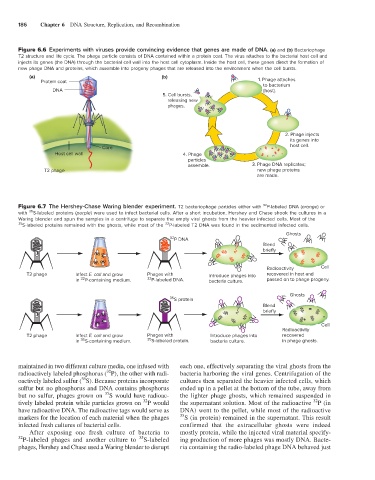
186 Chapter 6 DNA Structure, Replication, and Recombination
Figure 6.6 Experiments with viruses provide convincing evidence that genes are made of DNA. (a) and (b) Bacteriophage
T2 structure and life cycle. The phage particle consists of DNA contained within a protein coat. The virus attaches to the bacterial host cell and
injects its genes (the DNA) through the bacterial cell wall into the host cell cytoplasm. Inside the host cell, these genes direct the formation of
new phage DNA and proteins, which assemble into progeny phages that are released into the environment when the cell bursts.
(a) (b)
Protein coat 1. Phage attaches
to bacterium
DNA (host).
5. Cell bursts,
releasing new
phages.
2. Phage injects
its genes into
Core host cell.
Host cell wall 4. Phage
particles
assemble. 3. Phage DNA replicates;
T2 phage new phage proteins
are made.
32
Figure 6.7 The Hershey-Chase Waring blender experiment. T2 bacteriophage particles either with P-labeled DNA (orange) or
35
with S-labeled proteins (purple) were used to infect bacterial cells. After a short incubation, Hershey and Chase shook the cultures in a
Waring blender and spun the samples in a centrifuge to separate the empty viral ghosts from the heavier infected cells. Most of the
35 S-labeled proteins remained with the ghosts, while most of the P-labeled T2 DNA was found in the sedimented infected cells.
32
Ghosts
32
P DNA
Blend
briefly
Radioactivity Cell
T2 phage Infect E. coli and grow Phages with Introduce phages into recovered in host and
32
in P-containing medium. 32 P-labeled DNA. bacteria culture. passed on to phage progeny.
Ghosts
35
S protein
Blend
briefly
Cell
Radioactivity
T2 phage Infect E. coli and grow Phages with Introduce phages into recovered
35
in S-containing medium. 35 S-labeled protein. bacteria culture. in phage ghosts.
maintained in two different culture media, one infused with each one, effectively separating the viral ghosts from the
32
radioactively labeled phosphorus ( P), the other with radi- bacteria harboring the viral genes. Centrifugation of the
35
oactively labeled sulfur ( S). Because proteins incorporate cultures then separated the heavier infected cells, which
sulfur but no phosphorus and DNA contains phosphorus ended up in a pellet at the bottom of the tube, away from
35
but no sulfur, phages grown on S would have radioac- the lighter phage ghosts, which remained suspended in
32
32
tively labeled protein while particles grown on P would the supernatant solution. Most of the radioactive P (in
have radioactive DNA. The radioactive tags would serve as DNA) went to the pellet, while most of the radioactive
markers for the location of each material when the phages 35 S (in protein) remained in the supernatant. This result
infected fresh cultures of bacterial cells. confirmed that the extracellular ghosts were indeed
After exposing one fresh culture of bacteria to mostly protein, while the injected viral material specify-
35
32 P-labeled phages and another culture to S-labeled ing production of more phages was mostly DNA. Bacte-
phages, Hershey and Chase used a Waring blender to disrupt ria containing the radio-labeled phage DNA behaved just