Page 135 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part2
P. 135
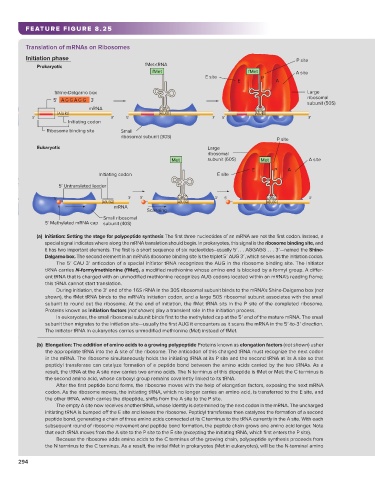
FEATURE FIGURE 8.25
Translation of mRNAs on Ribosomes
Initiation phase P site
Prokaryotic fMet•tRNA
fMet fMet A site
E site P
E A
Shine-Dalgarno box Large
5' AG GA GG 3' ribosomal
subunit (50S)
mRNA U A C U A C
AU G AU G AU G
5' 3' 5' 3' 5' 3'
Initiating codon
Ribosome binding site Small
ribosomal subunit (30S)
P site
Eukaryotic Large
ribosomal
Met subunit (60S) Met A site
E P A
Initiating codon E site
5' Untranslated leader
5' 3' 5' U A C 3' 5' U A C 3'
AU G AU G A UG
mRNA
Scanning
Small ribosomal
5' Methylated mRNA cap subunit (40S)
(a) Initiation: Setting the stage for polypeptide synthesis The first three nucleotides of an mRNA are not the first codon. Instead, a
special signal indicates where along the mRNA translation should begin. In prokaryotes, this signal is the ribosome binding site, and
it has two important elements. The first is a short sequence of six nucleotides–usually 5′. . . AGGAGG . . . 3′—named the Shine-
Dalgarno box. The second element in an mRNA’s ribosome binding site is the triplet 5′ AUG 3′, which serves as the initiation codon.
The 5′ CAU 3′ anticodon of a special initiator tRNA recognizes the AUG in the ribosome binding site. The initiator
tRNA carries N-formylmethionine (fMet), a modified methionine whose amino end is blocked by a formyl group. A differ-
ent tRNA that is charged with an unmodified methionine recognizes AUG codons located within an mRNA’s reading frame;
this tRNA cannot start translation.
During initiation, the 3′ end of the 16S rRNA in the 30S ribosomal subunit binds to the mRNA’s Shine-Dalgarno box (not
shown), the fMet tRNA binds to the mRNA’s initiation codon, and a large 50S ribosomal subunit associates with the small
subunit to round out the ribosome. At the end of initiation, the fMet tRNA sits in the P site of the completed ribosome.
Proteins known as initiation factors (not shown) play a transient role in the initiation process.
In eukaryotes, the small ribosomal subunit binds first to the methylated cap at the 5′ end of the mature mRNA. The small
subunit then migrates to the initiation site—usually the first AUG it encounters as it scans the mRNA in the 5′-to-3′ direction.
The initiator tRNA in eukaryotes carries unmodified methionine (Met) instead of fMet.
(b) Elongation: The addition of amino acids to a growing polypeptide Proteins known as elongation factors (not shown) usher
the appropriate tRNA into the A site of the ribosome. The anticodon of this charged tRNA must recognize the next codon
in the mRNA. The ribosome simultaneously holds the initiating tRNA at its P site and the second tRNA at its A site so that
peptidyl transferase can catalyze formation of a peptide bond between the amino acids carried by the two tRNAs. As a
result, the tRNA at the A site now carries two amino acids. The N terminus of this dipeptide is fMet or Met; the C terminus is
the second amino acid, whose carboxyl group remains covalently linked to its tRNA.
After the first peptide bond forms, the ribosome moves with the help of elongation factors, exposing the next mRNA
codon. As the ribosome moves, the initiating tRNA, which no lon ger carries an amino acid, is transferred to the E site, and
the other tRNA, which carries the dipeptide, shifts from the A site to the P site.
The empty A site now receives another tRNA, whose identity is determined by the next codon in the mRNA. The uncharged
initiating tRNA is bumped off the E site and leaves the ribosome. Peptidyl transferase then catalyzes the formation of a second
peptide bond, generating a chain of three amino acids connected at its C terminus to the tRNA currently in the A site. With each
subsequent round of ribosome movement and peptide bond formation, the peptide chain grows one amino acid longer. Note
that each tRNA moves from the A site to the P site to the E site (excepting the initiating tRNA, which first enters the P site).
Because the ribosome adds amino acids to the C terminus of the growing chain, polypeptide synthesis proceeds from
the N terminus to the C terminus. As a result, the initial fMet in prokaryotes (Met in eukaryotes), will be the N-terminal amino
294