Page 139 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part2
P. 139
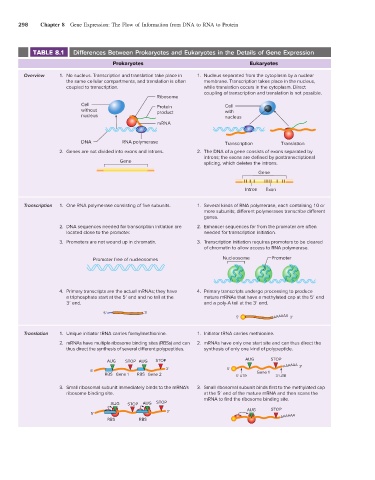
298 Chapter 8 Gene Expression: The Flow of Information from DNA to RNA to Protein
TABLE 8.1 Differences Between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes in the Details of Gene Expression
Prokaryotes Eukaryotes
Overview 1. No nucleus. Transcription and translation take place in 1. Nucleus separated from the cytoplasm by a nuclear
the same cellular compartments, and translation is often membrane. Transcription takes place in the nucleus,
coupled to transcription. while translation occurs in the cytoplasm. Direct
coupling of transcription and translation is not possible.
Ribosome
Cell Protein Cell
without product with
nucleus nucleus
mRNA
DNA RNA polymerase Transcription Translation
2. Genes are not divided into exons and introns. 2. The DNA of a gene consists of exons separated by
introns; the exons are defined by posttranscriptional
Gene splicing, which deletes the introns.
Gene
Intron Exon
Transcription 1. One RNA polymerase consisting of five subunits. 1. Several kinds of RNA polymerase, each containing 10 or
more subunits; different polymerases transcribe different
genes.
2. DNA sequences needed for transcription initiation are 2. Enhancer sequences far from the promoter are often
located close to the promoter. needed for transcription initiation.
3. Promoters are not wound up in chromatin. 3. Transcription initiation requires promoters to be cleared
of chromatin to allow access to RNA polymerase.
Promoter free of nucleosomes Nucleosome Promoter
4. Primary transcripts are the actual mRNAs; they have 4. Primary transcripts undergo processing to produce
a triphosphate start at the 5′ end and no tail at the mature mRNAs that have a methylated cap at the 5′ end
3′ end. and a poly-A tail at the 3′ end.
5' 3'
5' AAAAAA 3'
Translation 1. Unique initiator tRNA carries formylmethionine. 1. Initiator tRNA carries methionine.
2. mRNAs have multiple ribosome binding sites (RBSs) and can 2. mRNAs have only one start site and can thus direct the
thus direct the synthesis of several different polypeptides. synthesis of only one kind of polypeptide.
AUG STOP AUG STOP AUG STOP
AAAAAA 3'
3' 5'
5' Gene 1
RBS Gene 1 RBS Gene 2 5' UTR 3' UTR
3. Small ribosomal subunit immediately binds to the mRNA’s 3. Small ribosomal subunit binds first to the methylated cap
ribosome binding site. at the 5′ end of the mature mRNA and then scans the
mRNA to find the ribosome binding site.
AUG STOP AUG STOP
3' AUG STOP
5'
RBS RBS AAAAAA