Page 133 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part2
P. 133
292 Chapter 8 Gene Expression: The Flow of Information from DNA to RNA to Protein
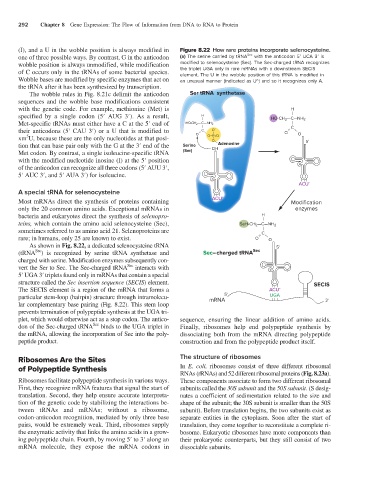
(I), and a U in the wobble position is always modified in Figure 8.22 How rare proteins incorporate selenocysteine.
one of three possible ways. By contrast, G in the anticodon (a) The serine carried by tRNA Sec with the anticodon 5′ UCA 3′ is
wobble position is always unmodified, while modification modified to selenocysteine (Sec). The Sec-charged tRNA recognizes
of C occurs only in the tRNAs of some bacterial species. the triplet UGA only in rare mRNAs with a downstream SECIS
element. The U in the wobble position of this tRNA is modified in
Wobble bases are modified by specific enzymes that act on an unusual manner (indicated as U^) and so it recognizes only A.
the tRNA after it has been synthesized by transcription.
The wobble rules in Fig. 8.21c delimit the anticodon Ser tRNA synthetase
sequences and the wobble base modifications consistent
with the genetic code. For example, methionine (Met) is H
—
specified by a single codon (5′ AUG 3′). As a result, H — HO-CH 2 —C—NH 2
Met-specific tRNAs must either have a C at the 5′ end of HO-CH 2 — C—NH 2 —
—
their anticodons (5′ CAU 3′) or a U that is modified to O = C — O - – O = C — O
5
xm U, because these are the only nucleotides at that posi- O–P O 5'
–
=
O —
tion that can base pair only with the G at the 3′ end of the Serine OH Adenosine
Met codon. By contrast, a single isoleucine-specific tRNA (Ser)
with the modified nucleotide inosine (I) at the 5′ position
of the anticodon can recognize all three codons (5′ AUU 3′,
5′ AUC 3′, and 5′ AUA 3′) for isoleucine.
ACUˆ
A special tRNA for selenocysteine
Most mRNAs direct the synthesis of proteins containing ACUˆ Modification
only the 20 common amino acids. Exceptional mRNAs in enzymes
bacteria and eukaryotes direct the synthesis of selenopro- H —
teins, which contain the amino acid selenocysteine (Sec), SeH-CH 2 —C—NH 2
sometimes referred to as amino acid 21. Selenoproteins are —
rare; in humans, only 25 are known to exist. O = C — O
As shown in Fig. 8.22, a dedicated selenocysteine tRNA 5'
Sec
(tRNA ) is recognized by serine tRNA synthetase and Sec–charged tRNA Sec
charged with serine. Modification enzymes subsequently con-
Sec
vert the Ser to Sec. The Sec-charged tRNA interacts with
5′ UGA 3′ triplets found only in mRNAs that contain a special
structure called the Sec insertion sequence (SECIS) element. SECIS
The SECIS element is a region of the mRNA that forms a ACUˆ
particular stem-loop (hairpin) structure through intramolecu- mRNA 5' UGA 3'
lar complementary base pairing (Fig. 8.22). This stem loop
prevents termination of polypeptide synthesis at the UGA tri-
plet, which would otherwise act as a stop codon. The antico- sequence, ensuring the linear addition of amino acids.
Sec
don of the Sec-charged tRNA binds to the UGA triplet in Finally, ribosomes help end polypeptide synthesis by
the mRNA, allowing the incorporation of Sec into the poly- dissociating both from the mRNA directing polypeptide
peptide product. construction and from the polypeptide product itself.
Ribosomes Are the Sites The structure of ribosomes
of Polypeptide Synthesis In E. coli, ribosomes consist of three different ribosomal
RNAs (rRNAs) and 52 different ribosomal proteins (Fig. 8.23a).
Ribosomes facilitate polypeptide synthesis in various ways. These components associate to form two different ribosomal
First, they recognize mRNA features that signal the start of subunits called the 30S subunit and the 50S subunit. (S desig-
translation. Second, they help ensure accurate interpreta- nates a coefficient of sedimentation related to the size and
tion of the genetic code by stabilizing the interactions be- shape of the subunit; the 30S subunit is smaller than the 50S
tween tRNAs and mRNAs; without a ribosome, subunit). Before translation begins, the two subunits exist as
codon-anticodon recognition, mediated by only three base separate entities in the cytoplasm. Soon after the start of
pairs, would be extremely weak. Third, ribosomes supply translation, they come together to reconstitute a complete ri-
the enzymatic activity that links the amino acids in a grow- bosome. Eukaryotic ribosomes have more components than
ing polypeptide chain. Fourth, by moving 5′ to 3′ along an their prokaryotic counterparts, but they still consist of two
mRNA molecule, they expose the mRNA codons in dissociable subunits.