Page 71 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part3
P. 71
PART III Analysis of Genetic Information
11
chapter
Analyzing Genomic
Variation
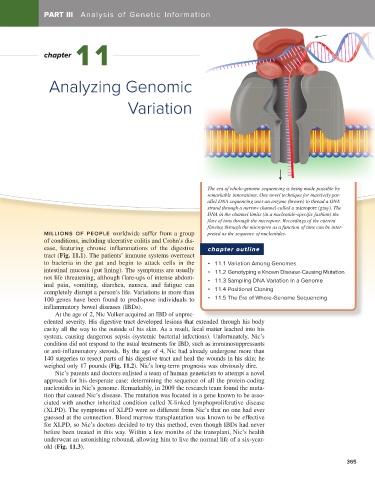
The era of whole-genome sequencing is being made possible by
remarkable innovations. One novel technique for massively par-
allel DNA sequencing uses an enzyme (brown) to thread a DNA
strand through a narrow channel called a micropore (gray). The
DNA in the channel limits (in a nucleotide-specific fashion) the
flow of ions through the micropore. Recordings of the current
flowing through the micropore as a function of time can be inter-
MILLIONS OF PEOPLE worldwide suffer from a group preted as the sequence of nucleotides.
of conditions, including ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s dis-
ease, featuring chronic inflammations of the digestive chapter outline
tract (Fig. 11.1). The patients’ immune systems overreact
to bacteria in the gut and begin to attack cells in the • 11.1 Variation Among Genomes
intestinal mucosa (gut lining). The symptoms are usually • 11.2 Genotyping a Known Disease-Causing Mutation
not life threatening, although flare-ups of intense abdom- • 11.3 Sampling DNA Variation in a Genome
inal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, nausea, and fatigue can
completely disrupt a person’s life. Variations in more than • 11.4 Positional Cloning
100 genes have been found to predispose individuals to • 11.5 The Era of Whole-Genome Sequencing
inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs).
At the age of 2, Nic Volker acquired an IBD of unprec-
edented severity. His digestive tract developed lesions that extended through his body
cavity all the way to the outside of his skin. As a result, fecal matter leached into his
system, causing dangerous sepsis (systemic bacterial infections). Unfortunately, Nic’s
condition did not respond to the usual treatments for IBD, such as immunosuppressants
or anti-inflammatory steroids. By the age of 4, Nic had already undergone more than
140 surgeries to resect parts of his digestive tract and heal the wounds in his skin; he
weighed only 17 pounds (Fig. 11.2). Nic’s long-term prognosis was obviously dire.
Nic’s parents and doctors enlisted a team of human geneticists to attempt a novel
approach for his desperate case: determining the sequence of all the protein-coding
nucleotides in Nic’s genome. Remarkably, in 2009 the research team found the muta-
tion that caused Nic’s disease. The mutation was located in a gene known to be asso-
ciated with another inherited condition called X-linked lymphoproliferative disease
(XLPD). The symptoms of XLPD were so different from Nic’s that no one had ever
guessed at the connection. Blood marrow transplantation was known to be effective
for XLPD, so Nic’s doctors decided to try this method, even though IBDs had never
before been treated in this way. Within a few months of the transplant, Nic’s health
underwent an astonishing rebound, allowing him to live the normal life of a six-year-
old (Fig. 11.3).
365