Page 94 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part1
P. 94
86 Chapter 3 Extensions to Mendel’s Laws
a. What can you conclude about the inheritance of Carpel Anther
the petal phenotypes in foxgloves?
b. Ascribe genotypes to the four true-breeding paren- Petal
tal strains (WR-1, WR-2, DR, and LR).
c. A WR plant from the F 2 generation of cross 1 is Sepal
now crossed with an LR plant. Of 500 total prog-
eny from this cross, there were 253 WR, 124 DR,
and 123 LR plants. What are the genotypes of the
parents in this WR × LR mating? Normal Mutant
43. In a culture of fruit flies, matings between any two © Sandra Biewers, www.sysflo.edu
flies with hairy wings (wings abnormally containing
additional small hairs along their edges) always pro- 45. A couple wants to know the probability that their ex-
duce both hairy-winged and normal-winged flies in a pected child will suffer from split-hand deformity,
2:1 ratio. You now take hairy-winged flies from this which affects the prospective father, who is indicated
culture and cross them with four types of normal- by an arrow in the pedigree shown. (The arrow means
winged flies; the results for each cross are shown in that he is the proband—the person in the family who
the following table. Assuming that only two possible first brought the disorder to the attention of medical
alleles of the hairy-winged gene exist (one for hairy professionals.) This trait, shown in the following
wings and one for normal wings), what can you say photo, is rare in the population, and the prospective
about the genotypes of the four types of normal- parents are not related to each other.
winged flies?
Progeny obtained from cross
with hairy-winged flies
Type of normal- Fraction with Fraction with
winged flies normal wings hairy wings
1 1/2 1/2 ?
2 1 0
3 3/4 1/4
4 2/3 1/3
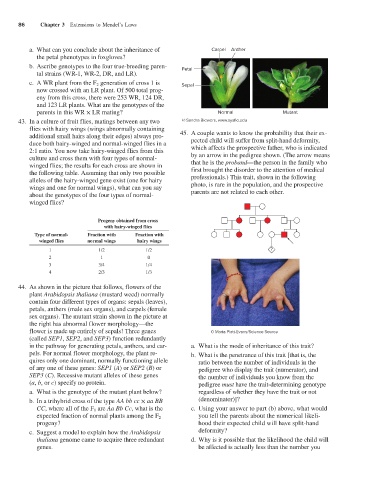
44. As shown in the picture that follows, flowers of the
plant Arabidopsis thaliana (mustard weed) normally
contain four different types of organs: sepals (leaves),
petals, anthers (male sex organs), and carpels (female
sex organs). The mutant strain shown in the picture at
the right has abnormal flower morphology—the
flower is made up entirely of sepals! Three genes © Maria Platt-Evans/Science Source
(called SEP1, SEP2, and SEP3) function redundantly
in the pathway for generating petals, anthers, and car- a. What is the mode of inheritance of this trait?
pels. For normal flower morphology, the plant re- b. What is the penetrance of this trait [that is, the
quires only one dominant, normally functioning allele ratio between the number of individuals in the
of any one of these genes: SEP1 (A) or SEP2 (B) or pedigree who display the trait (numerator), and
SEP3 (C). Recessive mutant alleles of these genes the number of individuals you know from the
(a, b, or c) specify no protein. pedigree must have the trait-determining genotype
a. What is the genotype of the mutant plant below? regardless of whether they have the trait or not
b. In a trihybrid cross of the type AA bb cc × aa BB (denominator)]?
CC, where all of the F 1 are Aa Bb Cc, what is the c. Using your answer to part (b) above, what would
expected fraction of normal plants among the F 2 you tell the parents about the numerical likeli-
progeny? hood their expected child will have split-hand
c. Suggest a model to explain how the Arabidopsis deformity?
thaliana genome came to acquire three redundant d. Why is it possible that the likelihood the child will
genes. be affected is actually less than the number you