Page 89 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part1
P. 89
Problems 81
e. How does this incompatibility system ensure that Homozygotes for nonfunctional mutant alleles do
all plants will be heterozygotes for different alleles not exist—they are never born. Describe the domi-
of the S gene? nance relation between the mutant and wild-type
f. How do you know that peas are not governed by alleles of SMARCAD1.
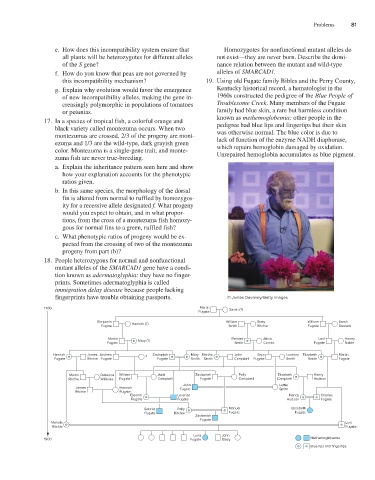
this incompatibility mechanism? 19. Using old Fugate family Bibles and the Perry County,
g. Explain why evolution would favor the emergence Kentucky historical record, a hematologist in the
of new incompatibility alleles, making the gene in- 1960s constructed the pedigree of the Blue People of
creasingly polymorphic in populations of tomatoes Troublesome Creek. Many members of the Fugate
or petunias. family had blue skin, a rare but harmless condition
17. In a species of tropical fish, a colorful orange and known as methemoglobemia; other people in the
pedigree had blue lips and fingertips but their skin
black variety called montezuma occurs. When two was otherwise normal. The blue color is due to
montezumas are crossed, 2/3 of the progeny are mont- lack of function of the enzyme NADH diaphorase,
ezuma and 1/3 are the wild-type, dark grayish green which repairs hemoglobin damaged by oxidation.
color. Montezuma is a single-gene trait, and monte- Unrepaired hemoglobin accumulates as blue pigment.
zuma fish are never true-breeding.
a. Explain the inheritance pattern seen here and show
how your explanation accounts for the phenotypic
ratios given.
b. In this same species, the morphology of the dorsal
fin is altered from normal to ruffled by homozygos-
ity for a recessive allele designated f. What progeny
would you expect to obtain, and in what propor-
tions, from the cross of a montezuma fish homozy-
gous for normal fins to a green, ruffled fish?
c. What phenotypic ratios of progeny would be ex-
pected from the crossing of two of the montezuma
progeny from part (b)?
18. People heterozygous for normal and nonfunctional
mutant alleles of the SMARCAD1 gene have a condi-
tion known as adermatoglyphia: they have no finger-
prints. Sometimes adermatoglyphia is called
immigration delay disease because people lacking
fingerprints have trouble obtaining passports. © James Devaney/Getty Images
1700 Martin Sarah (?)
Fugate
Benjamin Hannah (?) William Betty William Sarah
Fugate Smith Ritchie Fugate Stevens
Martin Richard Alicia Levi Haney
Fugate Mary (?) Smith Combs Fugate Noble
Hannah James Andrew Zachariah Mary Martha John Sara Lorenzo Elizabeth Martin
Fugate Ritchie Fugate ? Fugate Smith Smith Campbell Fugate Smith Smith Fugate
Martin Rebecca William Juda Zachariah Polly Elizabeth Henry
Ritchie Williams Fugate Campbell Fugate Campbell Campbell Hudson
John Lettie
James Hannah Fugate Smith
Ritchie Fugate
Eleanor Lorenzo Nancy Charles
Fugate Fugate Hudson Fugate
Gabriel Polly Manuel Elizabeth
Fugate Ritchie Fugate Fugate
Zachariah
Fugate
Mahala Levi
Ritchie Fugate
Luna John
1900 Fugate Stacy Methemoglobemia
Blue lips and fingertips