Page 150 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part1
P. 150
(a) Independent assortment
Orientation I
A
B
B
B
A
B
b
a
b
A
b
b
a
Meiosis I
B
A
B
a
B
A
B
a
A
b
a
b
A
a
b
b
A
A
a
142 Chapter 5 Linkage, Recombination, and the Mapping of Genes on Chromosomes Meiosis II a a a A Orientation II
B
B
B
B
a a A A
b
b
b
b
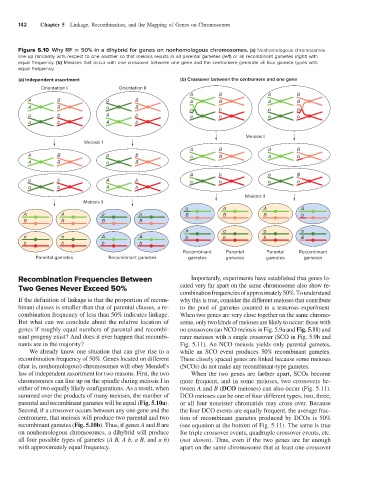
Figure 5.10 Why RF = 50% in a dihybrid for genes on nonhomologous chromosomes. (a) Nonhomologous chromosomes
line up randomly with respect to one another so that meiosis results in all parental gametes (left) or all recombinant gametes (right) with
equal frequency. (b) Meioses that occur with one crossover between one gene and the centromere generate all four gamete types with
Recombinant gametes
Parental gametes
equal frequency.
(a) Independent assortment (b) Crossover between the centromere and one gene
Orientation I Orientation II
A B A B
A B a B A B A B
A B a B a b a b
a b A b a b a b
a b A b
Meiosis I
Meiosis I
A B A B
A B a B a B A b
A B a B
A b a B
a b A b a b a b
a b A b
Meiosis II
Meiosis II
a A A A
A A a a B B B b
B B B B
A a a a
a a A A b b b B
b b b b
Recombinant Parental Parental Recombinant
Parental gametes Recombinant gametes gametes gametes gametes gametes
(b) Crossover between the centromere and one gene
Recombination Frequencies Between Importantly, experiments have established that genes lo-
Two Genes Never Exceed 50% B cated very far apart on the same chromosome also show re-
B
A
A
A B A B combination frequencies of approximately 50%. To understand
If the definition of linkage is that the proportion of recom- why this is true, consider the different meioses that contribute
b
a
b
a
binant classes is smaller than that of parental classes, a re- to the pool of gametes counted in a testcross experiment.
a
a
b
b
combination frequency of less than 50% indicates linkage. When two genes are very close together on the same chromo-
But what can we conclude about the relative location of some, only two kinds of meioses are likely to occur: those with
genes if roughly equal numbers of parental and recombi- no crossovers (an NCO meiosis in Fig. 5.9a and Fig. 5.11) and
Meiosis I
nant progeny exist? And does it ever happen that recombi- rarer meioses with a single crossover (SCO in Fig. 5.9b and
nants are in the majority? A B Fig. 5.11). An NCO meiosis yields only parental gametes,
B
A
A
a We already know one situation that can give rise to a while an SCO event produces 50% recombinant gametes.
B
b
recombination frequency of 50%. Genes located on different These closely spaced genes are linked because some meioses
(that is, nonhomologous) chromosomes will obey Mendel’s (NCOs) do not make any recombinant-type gametes.
B
A
b
a
law of independent assortment for two reasons. First, the two When the two genes are farther apart, SCOs become
b
b
a
a
chromosomes can line up on the spindle during meiosis I in more frequent, and in some meioses, two crossovers be-
either of two equally likely configurations. As a result, when tween A and B (DCO meioses) can also occur (Fig. 5.11).
Meiosis II
summed over the products of many meioses, the number of DCO meioses can be one of four different types; two, three,
parental and recombinant gametes will be equal (Fig. 5.10a). or all four nonsister chromatids may cross over. Because
A
A
A
a
Second, if a crossover occurs between any one gene and the the four DCO events are equally frequent, the average frac-
B
B
B
b
centromere, that meiosis will produce two parental and two tion of recombinant gametes produced by DCOs is 50%
recombinant gametes (Fig. 5.10b). Thus, if genes A and B are (see equation at the bottom of Fig. 5.11). The same is true
A
a
a
a
on nonhomologous chromosomes, a dihybrid will produce for triple crossover events, quadruple crossover events, etc.
b
B
b
b
all four possible types of gametes (A B, A b, a B, and a b) (not shown). Thus, even if the two genes are far enough
with approximately equal frequency. Recombinant apart on the same chromosome that at least one crossover
Parental
Parental
Recombinant
gametes gametes gametes gametes