Page 149 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part1
P. 149
5.2 Recombination: A Result of Crossing-Over During Meiosis 141
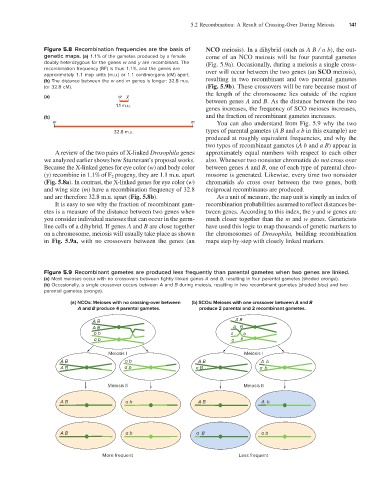
Figure 5.8 Recombination frequencies are the basis of NCO meiosis). In a dihybrid (such as A B / a b), the out-
genetic maps. (a) 1.1% of the gametes produced by a female come of an NCO meiosis will be four parental gametes
doubly heterozygous for the genes w and y are recombinant. The (Fig. 5.9a). Occasionally, during a meiosis a single cross-
recombination frequency (RF) is thus 1.1%, and the genes are over will occur between the two genes (an SCO meiosis),
approximately 1.1 map units (m.u.) or 1.1 centimorgans (cM) apart.
(b) The distance between the w and m genes is longer: 32.8 m.u. resulting in two recombinant and two parental gametes
(or 32.8 cM). (Fig. 5.9b). These crossovers will be rare because most of
the length of the chromosome lies outside of the region
(a) w y
between genes A and B. As the distance between the two
1.1 m.u. genes increases, the frequency of SCO meioses increases,
(b) and the fraction of recombinant gametes increases.
w m You can also understand from Fig. 5.9 why the two
32.8 m.u. types of parental gametes (A B and a b in this example) are
produced at roughly equivalent frequencies, and why the
two types of recombinant gametes (A b and a B) appear in
A review of the two pairs of X-linked Drosophila genes approximately equal numbers with respect to each other
we analyzed earlier shows how Sturtevant’s proposal works. also. Whenever two nonsister chromatids do not cross over
Because the X-linked genes for eye color (w) and body color between genes A and B, one of each type of parental chro-
(y) recombine in 1.1% of F 2 progeny, they are 1.1 m.u. apart mosome is generated. Likewise, every time two nonsister
(Fig. 5.8a). In contrast, the X-linked genes for eye color (w) chromatids do cross over between the two genes, both
and wing size (m) have a recombination frequency of 32.8 reciprocal recombinants are produced.
and are therefore 32.8 m.u. apart (Fig. 5.8b). As a unit of measure, the map unit is simply an index of
It is easy to see why the fraction of recombinant gam- recombination probabilities assumed to reflect distances be-
etes is a measure of the distance between two genes when tween genes. According to this index, the y and w genes are
you consider individual meioses that can occur in the germ- much closer together than the m and w genes. Geneticists
line cells of a dihybrid. If genes A and B are close together have used this logic to map thousands of genetic markers to
on a chromosome, meiosis will usually take place as shown the chromosomes of Drosophila, building recombination
in Fig. 5.9a, with no crossovers between the genes (an maps step-by-step with closely linked markers.
Figure 5.9 Recombinant gametes are produced less frequently than parental gametes when two genes are linked.
(a) Most meioses occur with no crossovers between tightly linked genes A and B, resulting in four parental gametes (shaded orange).
(b) Occasionally, a single crossover occurs between A and B during meiosis, resulting in two recombinant gametes (shaded blue) and two
parental gametes (orange).
(a) NCOs: Meioses with no crossing-over between (b) SCOs: Meioses with one crossover between A and B
A and B produce 4 parental gametes. produce 2 parental and 2 recombinant gametes.
A B A B
A B A B
a b a b
a b a b
Meiosis I Meiosis I
A B a b A B A b
A B a b a B a b
Meiosis II Meiosis II
A B a b A B A b
A B a b a B a b
More frequent Less frequent