Page 134 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part1
P. 134
126 Chapter 4 The Chromosome Theory of Inheritance
7. Indicate which of the cells numbered i–v matches c. The cells resulting from _____ in a haploid cell
each of the following stages of mitosis: have a ploidy of n.
a. anaphase d. The cells resulting from _____ in a diploid cell
b. prophase have a ploidy of n.
c. metaphase e. Homologous chromosome pairing regularly occurs
during _____.
d. G 2 f. Nonhomologous chromosome pairing regularly
e. telophase/cytokinesis occurs during _____.
i. ii. iii. g. Physical recombination leading to the production
of recombinant progeny classes occurs during
_____.
h. The separation of sister centromeres occurs during
iv. v.
_____.
i. Nonsister chromatids are found in the same cell
during _____.
14. The five cells shown in figures a–e are all from the same
8. a. What are the four major stages of the cell cycle? individual. For each cell, indicate whether it is in mitosis,
b. Which stages are included in interphase? meiosis I, or meiosis II. What stage of cell division is
c. What events distinguish G 1 , S, and G 2 ? represented in each case? What is n in this organism?
9. Answer the questions that follow for each stage of the a. d.
cell cycle (G 1 , S, G 2 , prophase, metaphase, anaphase,
telophase). If necessary, use an arrow to indicate a
change that occurs during a particular cell cycle stage
(for example, 1 → 2 or yes → no). b.
a. How many chromatids make up each chromosome e.
during this stage?
b. Is the nucleolus present?
c. Is the mitotic spindle organized? c.
d. Is the nuclear membrane present?
10. Can you think of anything that would prevent mitosis
from occurring in a cell whose genome is haploid?
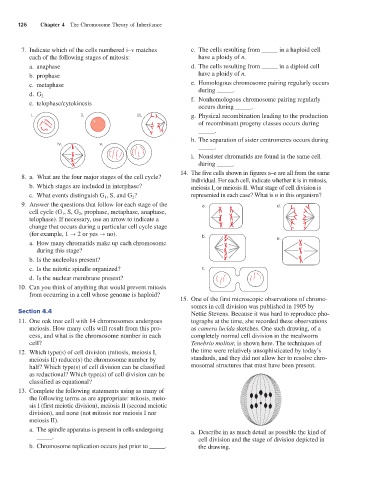
15. One of the first microscopic observations of chromo-
somes in cell division was published in 1905 by
Section 4.4 Nettie Stevens. Because it was hard to reproduce pho-
11. One oak tree cell with 14 chromosomes undergoes tographs at the time, she recorded these observations
meiosis. How many cells will result from this pro- as camera lucida sketches. One such drawing, of a
cess, and what is the chromosome number in each completely normal cell division in the mealworm
cell? Tenebrio molitor, is shown here. The techniques of
12. Which type(s) of cell division (mitosis, meiosis I, the time were relatively unsophisticated by today’s
meiosis II) reduce(s) the chromosome number by standards, and they did not allow her to resolve chro-
half? Which type(s) of cell division can be classified mosomal structures that must have been present.
as reductional? Which type(s) of cell division can be
classified as equational?
13. Complete the following statements using as many of
the following terms as are appropriate: mitosis, meio-
sis I (first meiotic division), meiosis II (second meiotic
division), and none (not mitosis nor meiosis I nor
meiosis II).
a. The spindle apparatus is present in cells undergoing a. Describe in as much detail as possible the kind of
_____. cell division and the stage of division depicted in
b. Chromosome replication occurs just prior to _____. the drawing.