Page 132 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part1
P. 132
124 Chapter 4 The Chromosome Theory of Inheritance
that the extra chromosome came from the father (the only Therefore, the nondisjunction occurred in meiosis II in
parent with a blobbed chromosome). the father.
Fetus Mother Father
II. (a) What sex ratio would you expect among the off-
spring of a cross between a normal male mouse and a
female mouse heterozygous for a recessive X-linked
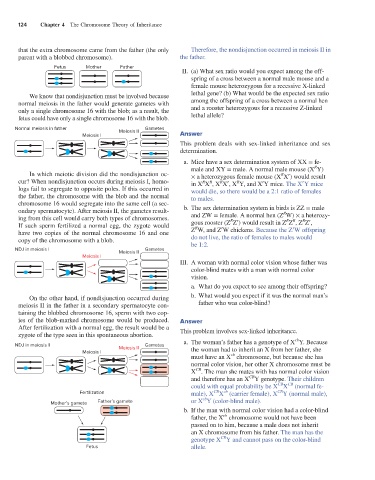
We know that nondisjunction must be involved because lethal gene? (b) What would be the expected sex ratio
normal meiosis in the father would generate gametes with among the offspring of a cross between a normal hen
only a single chromosome 16 with the blob; as a result, the and a rooster heterozygous for a recessive Z-linked
fetus could have only a single chromosome 16 with the blob. lethal allele?
Normal meiosis in father Meiosis II Gametes
Meiosis I Answer
This problem deals with sex-linked inheritance and sex
determination.
a. Mice have a sex determination system of XX = fe-
R
male and XY = male. A normal male mouse (X Y)
In which meiotic division did the nondisjunction oc- × a heterozygous female mouse (X X ) would result
R
r
cur? When nondisjunction occurs during meiosis I, homo- in X X , X X , X Y, and X Y mice. The X Y mice
r
R
r
R
R
r
R
logs fail to segregate to opposite poles. If this occurred in would die, so there would be a 2:1 ratio of females
the father, the chromosome with the blob and the normal to males.
chromosome 16 would segregate into the same cell (a sec-
ondary spermatocyte). After meiosis II, the gametes result- b. The sex determination system in birds is ZZ = male
R
ing from this cell would carry both types of chromosomes. and ZW = female. A normal hen (Z W) × a heterozy-
R R
R r
R r
If such sperm fertilized a normal egg, the zygote would gous rooster (Z Z ) would result in Z Z , Z Z ,
r
r
R
have two copies of the normal chromosome 16 and one Z W, and Z W chickens. Because the Z W offspring
copy of the chromosome with a blob. do not live, the ratio of females to males would
be 1:2.
NDJ in meiosis I Meiosis II Gametes
Meiosis I
III. A woman with normal color vision whose father was
color-blind mates with a man with normal color
vision.
a. What do you expect to see among their offspring?
On the other hand, if nondisjunction occurred during b. What would you expect if it was the normal man’s
meiosis II in the father in a secondary spermatocyte con- father who was color-blind?
taining the blobbed chromosome 16, sperm with two cop-
ies of the blob-marked chromosome would be produced. Answer
After fertilization with a normal egg, the result would be a This problem involves sex-linked inheritance.
zygote of the type seen in this spontaneous abortion.
cb
a. The woman’s father has a genotype of X Y. Because
NDJ in meiosis II Meiosis II Gametes
Meiosis I the woman had to inherit an X from her father, she
must have an X chromosome, but because she has
cb
normal color vision, her other X chromosome must be
X . The man she mates with has normal color vision
CB
and therefore has an X Y genotype. Their children
CB
CB
CB
could with equal probability be X X (normal fe-
CB
CB
cb
Fertilization male), X X (carrier female), X Y (normal male),
cb
Mother’s gamete Father’s gamete or X Y (color-blind male).
b. If the man with normal color vision had a color-blind
father, the X chromosome would not have been
cb
passed on to him, because a male does not inherit
an X chromosome from his father. The man has the
genotype X Y and cannot pass on the color-blind
CB
Fetus allele.