Page 139 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part1
P. 139
Problems 131
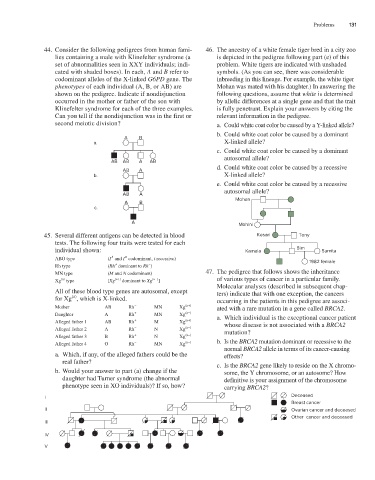
44. Consider the following pedigrees from human fami- 46. The ancestry of a white female tiger bred in a city zoo
lies containing a male with Klinefelter syndrome (a is depicted in the pedigree following part (e) of this
set of abnormalities seen in XXY individuals; indi- problem. White tigers are indicated with unshaded
cated with shaded boxes). In each, A and B refer to symbols. (As you can see, there was considerable
codominant alleles of the X-linked G6PD gene. The inbreeding in this lineage. For example, the white tiger
phenotypes of each individual (A, B, or AB) are Mohan was mated with his daughter.) In answering the
shown on the pedigree. Indicate if nondisjunction following questions, assume that white is determined
occurred in the mother or father of the son with by allelic differences at a single gene and that the trait
Klinefelter syndrome for each of the three examples. is fully penetrant. Explain your answers by citing the
Can you tell if the nondisjunction was in the first or relevant information in the pedigree.
second meiotic division? a. Could white coat color be caused by a Y-linked allele?
b. Could white coat color be caused by a dominant
A B
a. X-linked allele?
c. Could white coat color be caused by a dominant
autosomal allele?
AB AB A AB
d. Could white coat color be caused by a recessive
AB A
b. X-linked allele?
e. Could white coat color be caused by a recessive
autosomal allele?
AB A
Mohan
A B
c.
A Mohini
45. Several different antigens can be detected in blood Kesari Tony
tests. The following four traits were tested for each
individual shown: Kamala Bim Sumita
A
B
ABO type (I and I codominant, i recessive) 1982 female
−
+
Rh type (Rh dominant to Rh )
MN type (M and N codominant) 47. The pedigree that follows shows the inheritance
(a)
Xg type [Xg (a+) dominant to Xg (a−) ] of various types of cancer in a particular family.
Molecular analyses (described in subsequent chap-
All of these blood type genes are autosomal, except ters) indicate that with one exception, the cancers
(a)
for Xg , which is X-linked. occurring in the patients in this pedigree are associ-
Mother AB Rh − MN Xg (a+) ated with a rare mutation in a gene called BRCA2.
+
Daughter A Rh MN Xg (a−) a. Which individual is the exceptional cancer patient
+
Alleged father 1 AB Rh M Xg (a+) whose disease is not associated with a BRCA2
Alleged father 2 A Rh − N Xg (a−) mutation?
+
Alleged father 3 B Rh N Xg (a−)
Alleged father 4 O Rh − MN Xg (a−) b. Is the BRCA2 mutation dominant or recessive to the
normal BRCA2 allele in terms of its cancer-causing
a. Which, if any, of the alleged fathers could be the effects?
real father? c. Is the BRCA2 gene likely to reside on the X chromo-
b. Would your answer to part (a) change if the some, the Y chromosome, or an autosome? How
daughter had Turner syndrome (the abnormal definitive is your assignment of the chromosome
phenotype seen in XO individuals)? If so, how? carrying BRCA2?
Deceased
I
Breast cancer
II Ovarian cancer and deceased
Other cancer and deceased
III
IV
V