Page 118 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part1
P. 118
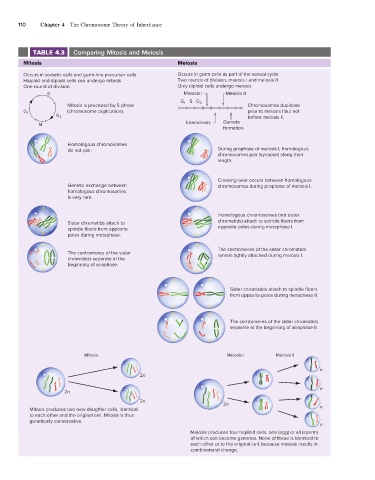
110 Chapter 4 The Chromosome Theory of Inheritance
TABLE 4.3 Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitosis Meiosis
Occurs in somatic cells and germ-line precursor cells Occurs in germ cells as part of the sexual cycle
Haploid and diploid cells can undergo mitosis Two rounds of division, meiosis I and meiosis II
One round of division Only diploid cells undergo meiosis
S Meiosis I Meiosis II
G 1 S G 2
Mitosis is preceded by S phase Chromosomes duplicate
(chromosome duplication). prior to meiosis I but not
G 1
G 2 before meiosis II.
Interkinesis Gamete
M
formation
Homologous chromosomes
do not pair. During prophase of meiosis I, homologous
chromosomes pair (synapse) along their
length.
Crossing-over occurs between homologous
Genetic exchange between chromosomes during prophase of meiosis I.
homologous chromosomes
is very rare.
Homologous chromosomes (not sister
Sister chromatids attach to chromatids) attach to spindle fibers from
spindle fibers from opposite opposite poles during metaphase I.
poles during metaphase.
The centromeres of the sister chromatids
The centromeres of the sister remain tightly attached during meiosis I.
chromatids separate at the
beginning of anaphase.
Sister chromatids attach to spindle fibers
from opposite poles during metaphase II.
The centromeres of the sister chromatids
separate at the beginning of anaphase II.
Mitosis Meiosis I Meiosis II
n
2n
n
2n
2n
2n
Mitosis produces two new daughter cells, identical n
to each other and the original cell. Mitosis is thus
genetically conservative.
n
Meiosis produces four haploid cells, one (egg) or all (sperm)
of which can become gametes. None of these is identical to
each other or to the original cell, because meiosis results in
combinatorial change.