Page 122 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part1
P. 122
114 Chapter 4 The Chromosome Theory of Inheritance
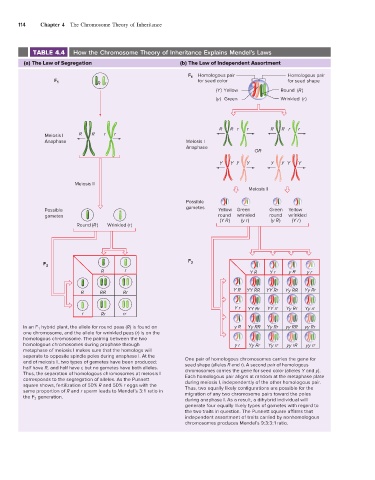
TABLE 4.4 How the Chromosome Theory of Inheritance Explains Mendel’s Laws
(a) The Law of Segregation (b) The Law of Independent Assortment
F 1 Homologous pair Homologous pair
F 1 Rr for seed color for seed shape
(Y) Yellow Round (R)
(y) Green Wrinkled (r)
R R r r R R r r
Meiosis I R R r r
Anaphase Meiosis I
Anaphase
OR
Y Y y y y y Y Y
Meiosis II
Meiosis II
Possible
gametes
Possible Yellow Green Green Yellow
gametes round wrinkled round wrinkled
(Y R) (y r) (y R) (Y r)
Round (R) Wrinkled (r)
F 2
F 2
R r Y R Y r y R y r
Y R YY RR YY Rr Yy RR Yy Rr
R RR Rr
Y r YY Rr YY rr Yy Rr Yy rr
r Rr rr
In an F 1 hybrid plant, the allele for round peas (R) is found on y R Yy RR Yy Rr yy RR yy Rr
one chromosome, and the allele for wrinkled peas (r) is on the
homologous chromosome. The pairing between the two
homologous chromosomes during prophase through y r Yy Rr Yy rr yy rR yy rr
metaphase of meiosis I makes sure that the homologs will
separate to opposite spindle poles during anaphase I. At the One pair of homologous chromosomes carries the gene for
end of meiosis II, two types of gametes have been produced: seed shape (alleles R and r). A second pair of homologous
half have R, and half have r, but no gametes have both alleles. chromosomes carries the gene for seed color (alleles Y and y).
Thus, the separation of homologous chromosomes at meiosis I Each homologous pair aligns at random at the metaphase plate
corresponds to the segregation of alleles. As the Punnett during meiosis I, independently of the other homologous pair.
square shows, fertilization of 50% R and 50% r eggs with the Thus, two equally likely configurations are possible for the
same proportion of R and r sperm leads to Mendel’s 3:1 ratio in migration of any two chromosome pairs toward the poles
the F 2 generation.
during anaphase I. As a result, a dihybrid individual will
generate four equally likely types of gametes with regard to
the two traits in question. The Punnett square affirms that
independent assortment of traits carried by nonhomologous
chromosomes produces Mendel’s 9:3:3:1 ratio.