Page 120 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part1
P. 120
112 Chapter 4 The Chromosome Theory of Inheritance
From the onset of puberty at about age 12, until meno- age and meiotic segregational errors, including those that
pause some 35–40 years later, most women release one pri- produce trisomies. Women in their mid-20s, for example,
mary oocyte each month (from alternate ovaries), amounting run a very small risk of trisomy 21; only 0.05% of children
to roughly 480 oocytes released during the reproductive born to women of this age have Down syndrome. During
years. The remaining primary oocytes disintegrate during the later childbearing years, however, the risk rises rapidly;
menopause. At ovulation, a released oocyte completes mei- at age 35, it is 0.9% of live births, and at age 45, it is 3%.
osis I and proceeds as far as the metaphase of meiosis II. If You would not expect this age-related increase in risk if
the oocyte is then fertilized, that is, penetrated by a sperm meiosis were completed before the mother’s birth.
nucleus, it quickly completes meiosis II. The nuclear mem-
branes of the sperm and ovum dissolve, allowing their chro-
mosomes to form the single diploid nucleus of the zygote, Spermatogenesis in Humans
and the zygote divides by mitosis to produce a functional Produces Four Sperm from Each
embryo. In contrast, unfertilized oocytes exit the body dur- Primary Spermatocyte
ing the menses stage of the menstrual cycle.
The long interval before completion of meiosis in oo- The production of sperm, or spermatogenesis (Fig. 4.19),
cytes released by women in their 30s, 40s, and 50s may begins in the male testes in germ cells known as
contribute to the observed correlation between maternal spermatogonia. Mitotic divisions of the spermatogonia
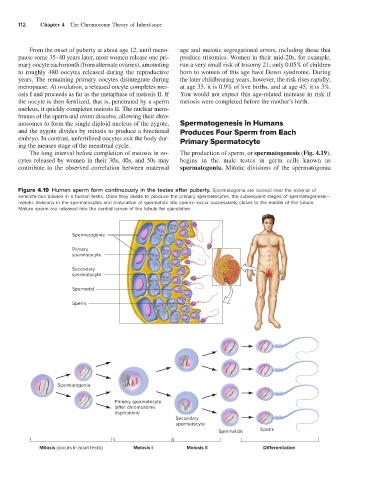
Figure 4.19 Human sperm form continuously in the testes after puberty. Spermatogonia are located near the exterior of
seminiferous tubules in a human testis. Once they divide to produce the primary spermatocytes, the subsequent stages of spermatogenesis—
meiotic divisions in the spermatocytes and maturation of spermatids into sperm—occur successively closer to the middle of the tubule.
Mature sperm are released into the central lumen of the tubule for ejaculation.
Spermatogonia
Primary
spermatocyte
Secondary
spermatocyte
Spermatid
Sperm
Spermatogonia
Primary spermatocyte
(after chromosome
duplication)
Secondary
spermatocyte
Spermatids Sperm
Mitosis (occurs in adult testis) Meiosis I Meiosis II Di erentiation