Page 119 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part1
P. 119
4.5 Gametogenesis 111
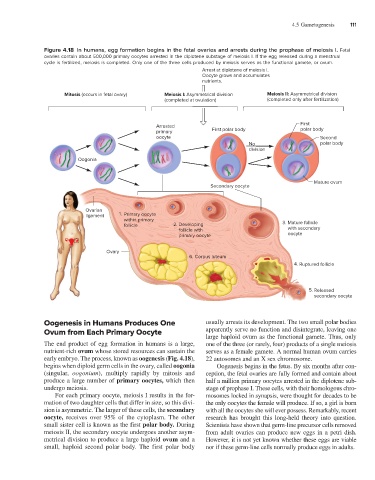
Figure 4.18 In humans, egg formation begins in the fetal ovaries and arrests during the prophase of meiosis I. Fetal
ovaries contain about 500,000 primary oocytes arrested in the diplotene substage of meiosis I. If the egg released during a menstrual
cycle is fertilized, meiosis is completed. Only one of the three cells produced by meiosis serves as the functional gamete, or ovum.
Arrest at diplotene of meiosis I.
Oocyte grows and accumulates
nutrients.
Mitosis (occurs in fetal ovary) Meiosis I: Asymmetrical division Meiosis II: Asymmetrical division
(completed at ovulation) (completed only after fertilization)
First
Arrested
primary First polar body polar body
oocyte Second
No polar body
division
Oogonia
Mature ovum
Secondary oocyte
Ovarian
ligament 1. Primary oocyte
within primary 3. Mature follicle
follicle 2. Developing
follicle with with secondary
primary oocyte oocyte
Ovary
6. Corpus luteum
4. Ruptured follicle
5. Released
secondary oocyte
Oogenesis in Humans Produces One usually arrests its development. The two small polar bodies
Ovum from Each Primary Oocyte apparently serve no function and disintegrate, leaving one
large haploid ovum as the functional gamete. Thus, only
The end product of egg formation in humans is a large, one of the three (or rarely, four) products of a single meiosis
nutrient-rich ovum whose stored resources can sustain the serves as a female gamete. A normal human ovum carries
early embryo. The process, known as oogenesis (Fig. 4.18), 22 autosomes and an X sex chromosome.
begins when diploid germ cells in the ovary, called oogonia Oogenesis begins in the fetus. By six months after con-
(singular, oogonium), multiply rapidly by mitosis and ception, the fetal ovaries are fully formed and contain about
produce a large number of primary oocytes, which then half a million primary oocytes arrested in the diplotene sub-
undergo meiosis. stage of prophase I. These cells, with their homologous chro-
For each primary oocyte, meiosis I results in the for- mosomes locked in synapsis, were thought for decades to be
mation of two daughter cells that differ in size, so this divi- the only oocytes the female will produce. If so, a girl is born
sion is asymmetric. The larger of these cells, the secondary with all the oocytes she will ever possess. Remarkably, recent
oocyte, receives over 95% of the cytoplasm. The other research has brought this long-held theory into question.
small sister cell is known as the first polar body. During Scientists have shown that germ-line precursor cells removed
meiosis II, the secondary oocyte undergoes another asym- from adult ovaries can produce new eggs in a petri dish.
metrical division to produce a large haploid ovum and a However, it is not yet known whether these eggs are viable
small, haploid second polar body. The first polar body nor if these germ-line cells normally produce eggs in adults.