Page 39 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part3
P. 39
9.4 Sequencing Genomes 333
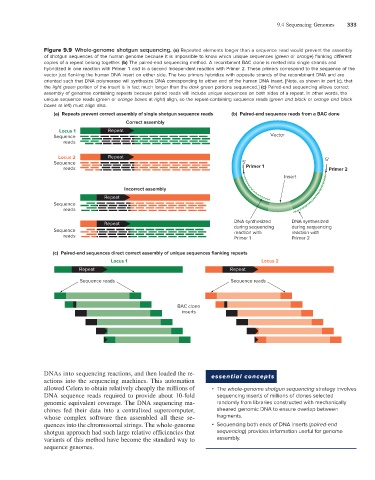
Figure 9.9 Whole-genome shotgun sequencing. (a) Repeated elements longer than a sequence read would prevent the assembly
of shotgun sequences of the human genome because it is impossible to know which unique sequences (green or orange) flanking different
copies of a repeat belong together. (b) The paired-end sequencing method. A recombinant BAC clone is melted into single strands and
hybridized in one reaction with Primer 1 and in a second independent reaction with Primer 2. These primers correspond to the sequence of the
vector just flanking the human DNA insert on either side. The two primers hybridize with opposite strands of the recombinant DNA and are
oriented such that DNA polymerase will synthesize DNA corresponding to either end of the human DNA insert. [Note, as shown in part (c), that
the light green portion of the insert is in fact much longer than the dark green portions sequenced.] (c) Paired-end sequencing allows correct
assembly of genomes containing repeats because paired reads will include unique sequences on both sides of a repeat. In other words, the
unique sequence reads (green or orange boxes at right) align, so the repeat-containing sequence reads (green and black or orange and black
boxes at left) must align also.
(a) Repeats prevent correct assembly of single shotgun sequence reads (b) Paired-end sequence reads from a BAC done
Correct assembly
Locus 1 Repeat
Sequence Vector
reads
Locus 2 Repeat 5'
Sequence 5'
reads Primer 1 Primer 2
Insert
Incorrect assembly
Repeat
Sequence
reads
Repeat DNA synthesized DNA synthesized
during sequencing
during sequencing
Sequence reaction with reaction with
reads Primer 1 Primer 2
(c) Paired-end sequences direct correct assembly of unique sequences flanking repeats
Locus 1 Locus 2
Repeat Repeat
Sequence reads Sequence reads
BAC clone
inserts
DNAs into sequencing reactions, and then loaded the re- essential concepts
actions into the sequencing machines. This automation
allowed Celera to obtain relatively cheaply the millions of • The whole-genome shotgun sequencing strategy involves
DNA sequence reads required to provide about 10-fold sequencing inserts of millions of clones selected
genomic equivalent coverage. The DNA sequencing ma- randomly from libraries constructed with mechanically
chines fed their data into a centralized supercomputer, sheared genomic DNA to ensure overlap between
whose complex software then assembled all these se- fragments.
quences into the chromosomal strings. The whole- genome • Sequencing both ends of DNA inserts (paired-end
shotgun approach had such large relative efficiencies that sequencing) provides information useful for genome
variants of this method have become the standard way to assembly.
sequence genomes.