Page 35 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part3
P. 35
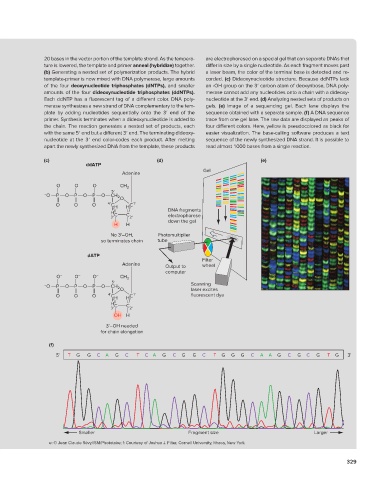
20 bases in the vector portion of the template strand. As the tempera- are electrophoresed on a special gel that can separate DNAs that
ture is lowered, the template and primer anneal (hybridize) together. differ in size by a single nucleotide. As each fragment moves past
(b) Generating a nested set of polymerization products. The hybrid a laser beam, the color of the terminal base is detected and re-
template-primer is now mixed with DNA polymerase, large amounts corded. (c) Dideoxynucleotide structure. Because ddNTPs lack
of the four deoxynucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs), and smaller an -OH group on the 3′ carbon atom of deoxyribose, DNA poly-
amounts of the four dideoxynucleotide triphosphates (ddNTPs). merase cannot add any nucleotides onto a chain with a dideoxy-
Each ddNTP has a fluorescent tag of a different color. DNA poly- nucleotide at the 3′ end. (d) Analyzing nested sets of products on
merase synthesizes a new strand of DNA complementary to the tem- gels. (e) Image of a sequencing gel. Each lane displays the
plate by adding nucleotides sequentially onto the 3′ end of the sequence obtained with a separate sample. (f) A DNA sequence
primer. Synthesis terminates when a dideoxynucleotide is added to trace from one gel lane. The raw data are displayed as peaks of
the chain. The reaction generates a nested set of products, each four different colors. Here, yellow is pseudocolored as black for
with the same 5′ end but a different 3′ end. The terminating dideoxy- easier visualization. The base-calling software produces a text
nucleotide at the 3′ end color-codes each product. After melting sequence of the newly synthesized DNA strand. It is possible to
apart the newly synthesized DNA from the template, these products read almost 1000 bases from a single reaction.
(c) (d) (e)
ddATP
Gel
Adenine
O – O – O – CH 2
5'
– O P O P O P O
CH 2
O
O O O 4' C H H C 1'
H DNA fragments
3' C C 2' electrophorese
down the gel
H H
No 3'–OH, Photomultiplier
so terminates chain tube
dATP
Filter
Adenine wheel
Output to
computer
O – O – O – CH 2
5'
– O P O P O P O CH 2 O Scanning
laser excites
O O O 4' C H H C 1' fluorescent dye
H C C
3' 2'
OH H
3'–OH needed
for chain elongation
(f)
5' T G G C A G C T C A G C G G C T G G G C A A G C G C G T G 3'
Smaller Fragment size Larger
e: © Jean Claude Révy/ISM/Phototake; f: Courtesy of Joshua J. Filter, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York
329