Page 38 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part3
P. 38
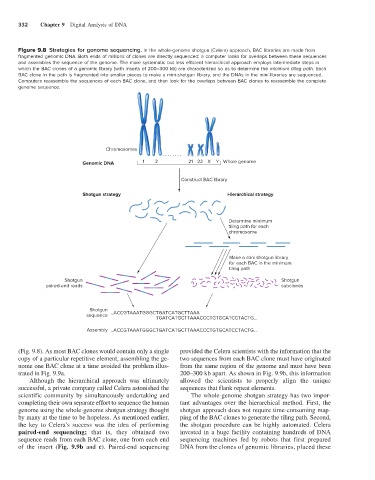
332 Chapter 9 Digital Analysis of DNA
Figure 9.8 Strategies for genome sequencing. In the whole-genome shotgun (Celera) approach, BAC libraries are made from
fragmented genomic DNA. Both ends of millions of clones are directly sequenced; a computer looks for overlaps between these sequences
and assembles the sequence of the genome. The more systematic but less efficient hierarchical approach employs intermediate steps in
which the BAC clones of a genomic library (with inserts of 200–300 kb) are characterized so as to determine the minimum tiling path. Each
BAC clone in the path is fragmented into smaller pieces to make a mini-shotgun library, and the DNAs in the mini-libraries are sequenced.
Computers reassemble the sequences of each BAC clone, and then look for the overlaps between BAC clones to reassemble the complete
genome sequence.
Chromosomes
........
Genomic DNA 1 2 21 22 X Y Whole genome
Construct BAC library
Shotgun strategy Hierarchical strategy
Determine minimum
tiling path for each
chromosome
Make a mini shotgun library
for each BAC in the minimum
tiling path
Shotgun Shotgun
paired-end reads subclones
Shotgun ...ACCGTAAATGGGCTGATCATGCTTAAA
sequence
TGATCATGCTTAAACCCTGTGCATCCTACTG...
Assembly ...ACCGTAAATGGGCTGATCATGCTTAAACCCTGTGCATCCTACTG...
(Fig. 9.8). As most BAC clones would contain only a single provided the Celera scientists with the information that the
copy of a particular repetitive element, assembling the ge- two sequences from each BAC clone must have originated
nome one BAC clone at a time avoided the problem illus- from the same region of the genome and must have been
trated in Fig. 9.9a. 200–300 kb apart. As shown in Fig. 9.9b, this information
Although the hierarchical approach was ultimately allowed the scientists to properly align the unique
successful, a private company called Celera astonished the sequences that flank repeat elements.
scientific community by simultaneously undertaking and The whole-genome shotgun strategy has two impor-
completing their own separate effort to sequence the human tant advantages over the hierarchical method. First, the
genome using the whole-genome shotgun strategy thought shotgun approach does not require time-consuming map-
by many at the time to be hopeless. As mentioned earlier, ping of the BAC clones to generate the tiling path. Second,
the key to Celera’s success was the idea of performing the shotgun procedure can be highly automated. Celera
paired-end sequencing; that is, they obtained two invested in a huge facility containing hundreds of DNA
sequence reads from each BAC clone, one from each end sequencing machines fed by robots that first prepared
of the insert (Fig. 9.9b and c). Paired-end sequencing DNA from the clones of genomic libraries, placed these