Page 47 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part2
P. 47
206 Chapter 6 DNA Structure, Replication, and Recombination
FEATURE FIGURE 6.27 (Continued)
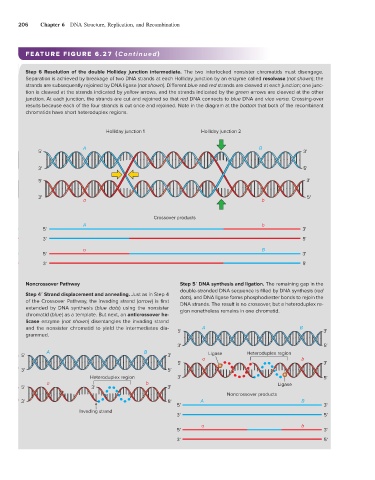
Step 6 Resolution of the double Holliday junction intermediate. The two interlocked nonsister chromatids must disengage.
Separation is achieved by breakage of two DNA strands at each Holliday junction by an enzyme called resolvase (not shown); the
strands are subsequently rejoined by DNA ligase (not shown). Different blue and red strands are cleaved at each junction; one junc-
tion is cleaved at the strands indicated by yellow arrows, and the strands indicated by the green arrows are cleaved at the other
junction. At each junction, the strands are cut and rejoined so that red DNA connects to blue DNA and vice versa. Crossing-over
results because each of the four strands is cut once and rejoined. Note in the diagram at the bottom that both of the recombinant
chromatids have short heteroduplex regions.
Holliday junction 1 Holliday junction 2
A B
5' 3'
3' 5'
5' 3'
3' 5'
a b
Crossover products
A b
5' 3'
3' 5'
a B
5' 3'
3' 5'
Noncrossover Pathway Step 5′ DNA synthesis and ligation. The remaining gap in the
double-stranded DNA sequence is filled by DNA synthesis (red
Step 4′ Strand displacement and annealing. Just as in Step 4 dots), and DNA ligase forms phosphodiester bonds to rejoin the
of the Crossover Pathway, the invading strand (arrow) is first DNA strands. The result is no crossover, but a heteroduplex re-
extended by DNA synthesis (blue dots) using the nonsister gion nonetheless remains in one chromatid.
chromatid (blue) as a template. But next, an anticrossover he-
licase enzyme (not shown) disentangles the invading strand
and the nonsister chromatid to yield the intermediates dia- 5' A B 3'
grammed.
3' 5'
A B Ligase Heteroduplex region
5' 3'
a b
5' 3'
3' 5'
Heteroduplex region 3' 5'
a b Ligase
5' 3' 3'
Noncrossover products
3' 5' A B
5' 3'
Invading strand
3' 5'
a b
5' 3'
3' 5'