Page 45 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part2
P. 45
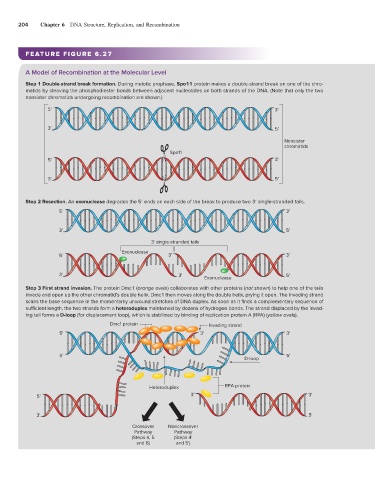
204 Chapter 6 DNA Structure, Replication, and Recombination
FEATURE FIGURE 6.27
A Model of Recombination at the Molecular Level
Step 1 Double-strand break formation. During meiotic prophase, Spo11 protein makes a double-strand break on one of the chro-
matids by cleaving the phosphodiester bonds between adjacent nucleotides on both strands of the DNA. (Note that only the two
nonsister chromatids undergoing recombination are shown.)
5' 3'
3' 5'
Nonsister
chromatids
Spo11
5' 3'
3' 5'
Step 2 Resection. An exonuclease degrades the 5′ ends on each side of the break to produce two 3′ single-stranded tails.
5' 3'
3' 5'
3' single-stranded tails
Exonuclease
5' 3' 3'
3' 3' Exonuclease 5'
Step 3 First strand invasion. The protein Dmc1 (orange ovals) collaborates with other proteins (not shown) to help one of the tails
invade and open up the other chromatid’s double helix. Dmc1 then moves along the double helix, prying it open. The invading strand
scans the base sequence in the momentarily unwound stretches of DNA duplex. As soon as it finds a complementary sequence of
sufficient length, the two strands form a heteroduplex maintained by dozens of hydrogen bonds. The strand displaced by the invad-
ing tail forms a D-loop (for displacement loop), which is stabilized by binding of replication protein A (RPA) (yellow ovals).
Dmc1 protein Invading strand
5' 3' 3'
3' 5'
D-loop
Heteroduplex RPA protein
5' 3' 3'
3' 5'
Crossover Noncrossover
Pathway Pathway
(Steps 4, 5 (Steps 4'
and 6) and 5')