Page 110 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part1
P. 110
102 Chapter 4 The Chromosome Theory of Inheritance
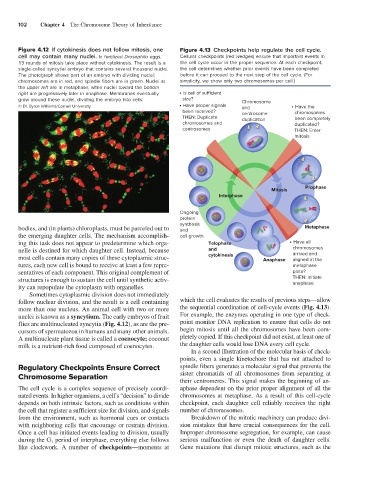
Figure 4.12 If cytokinesis does not follow mitosis, one Figure 4.13 Checkpoints help regulate the cell cycle.
cell may contain many nuclei. In fertilized Drosophila eggs, Cellular checkpoints (red wedges) ensure that important events in
13 rounds of mitosis take place without cytokinesis. The result is a the cell cycle occur in the proper sequence. At each checkpoint,
single-celled syncytial embryo that contains several thousand nuclei. the cell determines whether prior events have been completed
The photograph shows part of an embryo with dividing nuclei; before it can proceed to the next step of the cell cycle. (For
chromosomes are in red, and spindle fibers are in green. Nuclei at simplicity, we show only two chromosomes per cell.)
the upper left are in metaphase, while nuclei toward the bottom
right are progressively later in anaphase. Membranes eventually • Is cell of sucient
grow around these nuclei, dividing the embryo into cells. size? Chromosome
© Dr. Byron Williams/Cornell University • Have proper signals and • Have the
been received? centrosome chromosomes
THEN: Duplicate duplication been completely
chromosomes and duplicated?
centrosomes THEN: Enter
mitosis
Prophase
Mitosis
Interphase
Ongoing
protein
synthesis
bodies, and (in plants) chloroplasts, must be parceled out to and Metaphase
the emerging daughter cells. The mechanism accomplish- cell growth
ing this task does not appear to predetermine which orga- Telophase • Have all
nelle is destined for which daughter cell. Instead, because and chromosomes
arrived and
most cells contain many copies of these cytoplasmic struc- cytokinesis Anaphase aligned at the
tures, each new cell is bound to receive at least a few repre- metaphase
sentatives of each component. This original complement of plate?
structures is enough to sustain the cell until synthetic activ- THEN: Initiate
anaphase
ity can repopulate the cytoplasm with organelles.
Sometimes cytoplasmic division does not immediately
follow nuclear division, and the result is a cell containing which the cell evaluates the results of previous steps—allow
more than one nucleus. An animal cell with two or more the sequential coordination of cell-cycle events (Fig. 4.13).
nuclei is known as a syncytium. The early embryos of fruit For example, the enzymes operating in one type of check-
flies are multinucleated syncytia (Fig. 4.12), as are the pre- point monitor DNA replication to ensure that cells do not
cursors of spermatozoa in humans and many other animals. begin mitosis until all the chromosomes have been com-
A multinucleate plant tissue is called a coenocyte; coconut pletely copied. If this checkpoint did not exist, at least one of
milk is a nutrient-rich food composed of coenocytes. the daughter cells would lose DNA every cell cycle.
In a second illustration of the molecular basis of check-
points, even a single kinetochore that has not attached to
Regulatory Checkpoints Ensure Correct spindle fibers generates a molecular signal that prevents the
Chromosome Separation sister chromatids of all chromosomes from separating at
their centromeres. This signal makes the beginning of an-
The cell cycle is a complex sequence of precisely coordi- aphase dependent on the prior proper alignment of all the
nated events. In higher organisms, a cell’s “decision” to divide chromosomes at metaphase. As a result of this cell-cycle
depends on both intrinsic factors, such as conditions within checkpoint, each daughter cell reliably receives the right
the cell that register a sufficient size for division, and signals number of chromosomes.
from the environment, such as hormonal cues or contacts Breakdown of the mitotic machinery can produce divi-
with neighboring cells that encourage or restrain division. sion mistakes that have crucial consequences for the cell.
Once a cell has initiated events leading to division, usually Improper chromosome segregation, for example, can cause
during the G 1 period of interphase, everything else follows serious malfunction or even the death of daughter cells.
like clockwork. A number of checkpoints—moments at Gene mutations that disrupt mitotic structures, such as the