Page 112 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part1
P. 112
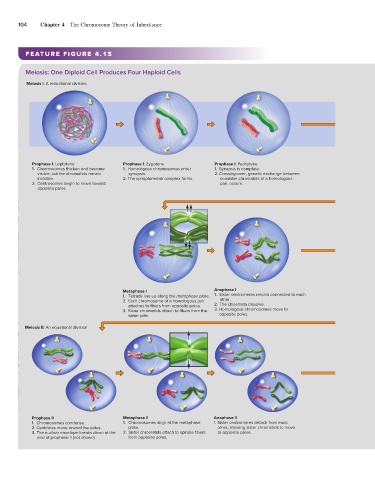
104 Chapter 4 The Chromosome Theory of Inheritance
FEATURE FIGURE 4.15
Meiosis: One Diploid Cell Produces Four Haploid Cells
Meiosis I: A reductional division
Prophase I: Leptotene Prophase I: Zygotene Prophase I: Pachytene
1. Chromosomes thicken and become 1. Homologous chromosomes enter 1. Synapsis is complete.
visible, but the chromatids remain synapsis. 2. Crossing-over, genetic exchange between
invisible. 2. The synaptonemal complex forms. nonsister chromatids of a homologous
2. Centrosomes begin to move toward pair, occurs.
opposite poles.
Metaphase I Anaphase I
1. Tetrads line up along the metaphase plate. 1. Sister centromeres remain connected to each
2. Each chromosome of a homologous pair other.
attaches to fibers from opposite poles. 2. The chiasmata dissolve.
3. Sister chromatids attach to fibers from the 3. Homologous chromosomes move to
same pole. opposite poles.
Meiosis II: An equational division
Prophase II Metaphase II Anaphase II
1. Chromosomes condense. 1. Chromosomes align at the metaphase 1. Sister centromeres detach from each
2. Centrioles move toward the poles. plate. other, allowing sister chromatids to move
3. The nuclear envelope breaks down at the 2. Sister chromatids attach to spindle fibers to opposite poles.
end of prophase II (not shown). from opposite poles.