Page 97 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part3
P. 97
11.5 The Era of Whole-Genome Sequencing 391
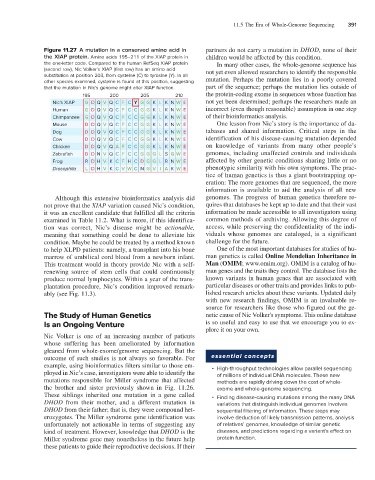
Figure 11.27 A mutation in a conserved amino acid in partners do not carry a mutation in DHOD, none of their
the XIAP protein. Amino acids 195–211 of the XIAP protein in children would be affected by this condition.
the one-letter code. Compared to the human RefSeq XIAP protein In many other cases, the whole-genome sequence has
(second row), Nic Volker’s XIAP (first row) has an amino acid not yet even allowed researchers to identify the responsible
substitution at position 203, from cysteine (C) to tyrosine (Y). In all
other species examined, cysteine is found at this position, suggesting mutation. Perhaps the mutation lies in a poorly covered
that the mutation in Nic’s genome might alter XIAP function. part of the sequence; perhaps the mutation lies outside of
195 200 205 210 the protein-coding exome in sequences whose function has
Nic’s XIAP G D Q V Q C F C Y G G K L K N W E not yet been determined; perhaps the researchers made an
Human G D Q V Q C F C C G G K L K N W E incorrect (even though reasonable) assumption in one step
Chimpanzee G D Q V Q C F C C G G K L K N W E of their bioinformatics analysis.
Mouse D D Q V Q C F C C G G K L K N W E One lesson from Nic’s story is the importance of da-
Dog D D Q V Q C F C C G G K L K N W E tabases and shared information. Critical steps in the
Cow D D Q V Q C F C C G G K L K N W E identification of his disease-causing mutation depended
Chicken D D Q V Q A F C C G G K L K N W E on knowledge of variants from many other people’s
Zebrafish D D N V Q C F C C G G G L S G W E genomes, including unaffected controls and individuals
Frog R D H V K C F H C D G G L R N W E affected by other genetic conditions sharing little or no
Drosophila L D H V K C V W C N G V I A K W E phenotypic similarity with his own symptoms. The prac-
tice of human genetics is thus a giant bootstrapping op-
eration: The more genomes that are sequenced, the more
information is available to aid the analysis of all new
Although this extensive bioinformatics analysis did genomes. The progress of human genetics therefore re-
not prove that the XIAP variation caused Nic’s condition, quires that databases be kept up to date and that their vast
it was an excellent candidate that fulfilled all the criteria information be made accessible to all investigators using
examined in Table 11.2. What is more, if this identifica- common methods of archiving. Allowing this degree of
tion was correct, Nic’s disease might be actionable, access, while preserving the confidentiality of the indi-
meaning that something could be done to alleviate his viduals whose genomes are cataloged, is a significant
condition. Maybe he could be treated by a method known challenge for the future.
to help XLPD patients: namely, a transplant into his bone One of the most important databases for studies of hu-
marrow of umbilical cord blood from a newborn infant. man genetics is called Online Mendelian Inheritance in
This treatment would in theory provide Nic with a self- Man (OMIM; www.omim.org). OMIM is a catalog of hu-
renewing source of stem cells that could continuously man genes and the traits they control. The database lists the
produce normal lymphocytes. Within a year of the trans- known variants in human genes that are associated with
plantation procedure, Nic’s condition improved remark- particular diseases or other traits and provides links to pub-
ably (see Fig. 11.3). lished research articles about these variants. Updated daily
with new research findings, OMIM is an invaluable re-
source for researchers like those who figured out the ge-
The Study of Human Genetics netic cause of Nic Volker's symptoms. This online database
Is an Ongoing Venture is so useful and easy to use that we encourage you to ex-
plore it on your own.
Nic Volker is one of an increasing number of patients
whose suffering has been ameliorated by information
gleaned from whole-exome/genome sequencing. But the
outcome of such studies is not always so favorable. For essential concepts
example, using bioinformatics filters similar to those em- • High-throughput technologies allow parallel sequencing
ployed in Nic’s case, investigators were able to identify the of millions of individual DNA molecules. These new
mutations responsible for Miller syndrome that affected methods are rapidly driving down the cost of whole-
the brother and sister previously shown in Fig. 11.26. exome and whole-genome sequencing.
These siblings inherited one mutation in a gene called • Finding disease-causing mutations among the many DNA
DHOD from their mother, and a different mutation in variations that distinguish individual genomes involves
DHOD from their father; that is, they were compound het- sequential filtering of information. These steps may
erozygotes. The Miller syndrome gene identification was involve deduction of likely transmission patterns, analysis
unfortunately not actionable in terms of suggesting any of relatives’ genomes, knowledge of similar genetic
kind of treatment. However, knowledge that DHOD is the diseases, and predictions regarding a variant’s effect on
Miller syndrome gene may nonetheless in the future help protein function.
these patients to guide their reproductive decisions. If their