Page 34 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part1
P. 34
26 Chapter 2 Mendel’s Principles of Heredity
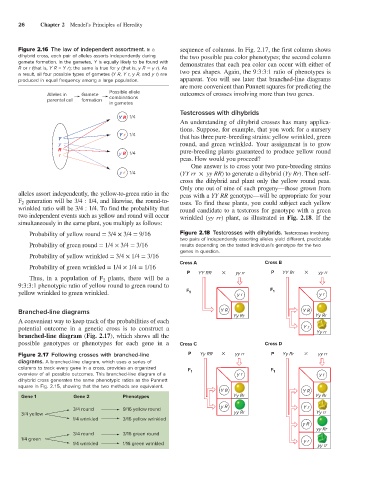
Figure 2.16 The law of independent assortment. In a sequence of columns. In Fig. 2.17, the first column shows
dihybrid cross, each pair of alleles assorts independently during the two possible pea color phenotypes; the second column
gamete formation. In the gametes, Y is equally likely to be found with demonstrates that each pea color can occur with either of
R or r (that is, Y R = Y r); the same is true for y (that is, y R = y r). As two pea shapes. Again, the 9:3:3:1 ratio of phenotypes is
a result, all four possible types of gametes (Y R, Y r, y R, and y r) are
produced in equal frequency among a large population. apparent. You will see later that branched-line diagrams
are more convenient than Punnett squares for predicting the
Possible allele
Alleles in Gamete outcomes of crosses involving more than two genes.
parental cell formation combinations
in gametes
Testcrosses with dihybrids
Y R 1/4
An understanding of dihybrid crosses has many applica-
tions. Suppose, for example, that you work for a nursery
Y r 1/4 that has three pure-breeding strains: yellow wrinkled, green
Y
y round, and green wrinkled. Your assignment is to grow
R pure-breeding plants guaranteed to produce yellow round
r y R 1/4
peas. How would you proceed?
One answer is to cross your two pure-breeding strains
y r 1/4 (YY rr × yy RR) to generate a dihybrid (Yy Rr). Then self-
cross the dihybrid and plant only the yellow round peas.
Only one out of nine of such progeny—those grown from
alleles assort independently, the yellow-to-green ratio in the peas with a YY RR genotype—will be appropriate for your
F 2 generation will be 3/4 : 1/4, and likewise, the round-to- uses. To find these plants, you could subject each yellow
wrinkled ratio will be 3/4 : 1/4. To find the probability that round candidate to a testcross for genotype with a green
two independent events such as yellow and round will occur wrinkled (yy rr) plant, as illustrated in Fig. 2.18. If the
simultaneously in the same plant, you multiply as follows:
Probability of yellow round = 3/4 × 3/4 = 9/16 Figure 2.18 Testcrosses with dihybrids. Testcrosses involving
two pairs of independently assorting alleles yield different, predictable
Probability of green round = 1/4 × 3/4 = 3/16 results depending on the tested individual’s genotype for the two
genes in question.
Probability of yellow wrinkled = 3/4 × 1/4 = 3/16
Cross A Cross B
Probability of green wrinkled = 1/4 × 1/4 = 1/16
P YY RR yy rr P YY Rr yy rr
Thus, in a population of F 2 plants, there will be a
9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio of yellow round to green round to
yellow wrinkled to green wrinkled. F 1 y r F 1 y r
Branched-line diagrams Y R Y R
Yy Rr Yy Rr
A convenient way to keep track of the probabilities of each
potential outcome in a genetic cross is to construct a Y r
branched-line diagram (Fig. 2.17), which shows all the Yy rr
possible genotypes or phenotypes for each gene in a Cross C Cross D
Figure 2.17 Following crosses with branched-line P Yy RR yy rr P Yy Rr yy rr
diagrams. A branched-line diagram, which uses a series of
columns to track every gene in a cross, provides an organized F 1 F 1
overview of all possible outcomes. This branched-line diagram of a y r y r
dihybrid cross generates the same phenotypic ratios as the Punnett
square in Fig. 2.15, showing that the two methods are equivalent.
Y R Y R
Gene 1 Gene 2 Phenotypes Yy Rr Yy Rr
y R Y r
3/4 round 9/16 yellow round
3/4 yellow yy Rr Yy rr
1/4 wrinkled 3/16 yellow wrinkled
y R
yy Rr
3/4 round 3/16 green round
1/4 green y r
1/4 wrinkled 1/16 green wrinkled yy rr