Page 116 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part2
P. 116
8.1 The Genetic Code 275
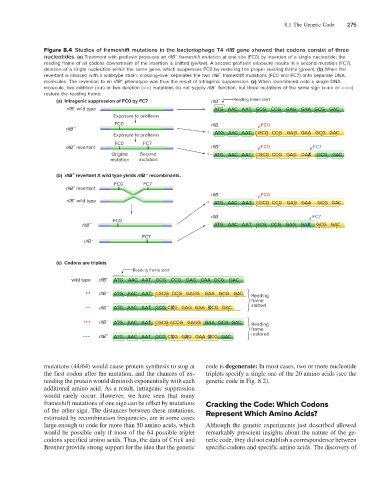
Figure 8.4 Studies of frameshift mutations in the bacteriophage T4 rIIB gene showed that codons consist of three
−
nucleotides. (a) Treatment with proflavin produces an rIIB frameshift mutation at one site (FC0) by insertion of a single nucleotide; the
reading frame of all codons downstream of the insertion is shifted (yellow). A second proflavin exposure results in a second mutation (FC7),
deletion of a single nucleotide within the same gene, which suppresses FC0 by restoring the proper reading frame (green). (b) When the
−
revertant is crossed with a wild-type strain, crossing-over separates the two rIIB frameshift mutations (FC0 and FC7) onto separate DNA
molecules. The reversion to an rIIB phenotype was thus the result of intragenic suppression. (c) When recombined onto a single DNA
+
+
molecule, two addition (++) or two deletion (−−) mutations do not supply rIIB function, but three mutations of the same sign (+++ or −−−)
restore the reading frame.
(a) Intragenic suppression of FC0 by FC7 rIIB + Reading frame start
+
rIIB wild type ATG AAC AAT GCG CCG GAG GAA GCG GAC
Exposure to proflavin
FC0 rIIB FC0
–
–
rIIB
Exposure to proflavin + ATG AAC AAT CGCG CC G GAG GAA GCG GAC
FC0 FC7 +
+
rIIB revertant rIIB FC0 FC7
Original Second + – ATG AAC AAT CGCG CC G GAG GAA GCG GAC
mutation mutation
–
+
(b) rIIB revertant X wild type yields rIIB recombinants.
FC0 FC7
+
rIIB revertant
–
rIIB FC0
+
rIIB wild type + ATG AAC AAT CGCG CC G GAG GAA GCG GAC
–
rIIB FC7
FC0
rIIB – – ATG AAC AAT GCG CC G GAG GAA GCG GAC
FC7
rIIB –
(c) Codons are triplets
Reading frame start
wild type rIIB + ATG AAC AAT GCG CCG GAG GAA GCG GAC
–
++ rIIB ATG AAC AAT CGCG CC G GAGG GAA GCG GAC Reading
frame
–
–– rIIB ATG AAC AAT GCG CC G GAG GAA GCG GAC shifted
+++ rIIB + ATG AAC AAT CGCG ACC G GAGG GAA GCG GAC Reading
frame
––– rIIB + ATG AAC AAT GCG CC G GAG GAA GCG GAC restored
mutations (44/64) would cause protein synthesis to stop at code is degenerate: In most cases, two or more nucleotide
the first codon after the mutation, and the chances of ex triplets specify a single one of the 20 amino acids (see the
tending the protein would diminish exponentially with each genetic code in Fig. 8.2).
additional amino acid. As a result, intragenic suppression
would rarely occur. However, we have seen that many
frameshift mutations of one sign can be offset by mutations Cracking the Code: Which Codons
of the other sign. The distances between these mutations, Represent Which Amino Acids?
estimated by recombination frequencies, are in some cases
large enough to code for more than 50 amino acids, which Although the genetic experiments just described allowed
would be possible only if most of the 64 possible triplet remarkably prescient insights about the nature of the ge
codons specified amino acids. Thus, the data of Crick and netic code, they did not establish a correspondence between
Brenner provide strong support for the idea that the genetic specific codons and specific amino acids. The discovery of