Page 15 - Chromosome_genes_DNA_FULL
P. 15
2
U
C
A
G
Tyrosine
Serine
Tyrosine
Cysteine
C
Serine
Phenylalanine
Stop
Leucine
Stop
Serine
A
Leucine
Serine
Stop
G
Tryptophan
Proline
U
Arginine
Histidine
Leucine
C
Proline
Leucine
C
Histidine
Arginine
Proline
Glutamine
Leucine
Arginine
A
Leucine
G
Glutamine
Proline
Arginine
Asparagine
Isoleucine
Serine
Threonine
U
A
Threonine
C
Asparagine
Isoleucine
Serine
Lysine
Threonine
Arginine
A
Isoleucine
Lysine
Arginine
G
Methionine
Threonine
L 1 U Phenylalanine The Genetic Code Cysteine U 3
Alanine
Aspartic acid
Glycine
U
Valine
T G C G Valine Alanine Aspartic acid Glycine C
Alanine
Glycine
A
Valine
Glutamic acid
Valine Alanine Glutamic acid Glycine G
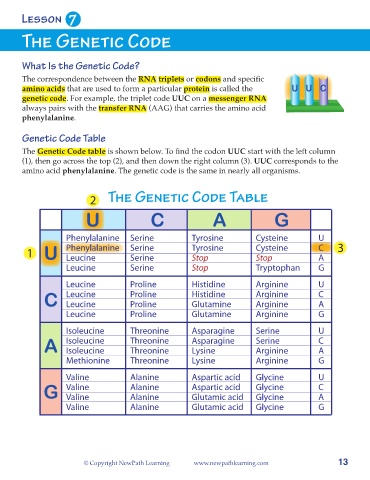
What Is the Genetic Code?
The correspondence between the RNA triplets or codons and specific
amino acids that are used to form a particular protein is called the U U C
genetic code. For example, the triplet code UUC on a messenger RNA
always pairs with the transfer RNA (AAG) that carries the amino acid
phenylalanine.
Genetic Code Table
The Genetic Code table is shown below. To find the codon UUC start with the left column
(1), then go across the top (2), and then down the right column (3). UUC corresponds to the
amino acid phenylalanine. The genetic code is the same in nearly all organisms.
The Genetic Code
2 T G C T
U C A G
Phenylalanine Serine Tyrosine Cysteine U
1 U Phenylalanine Serine Tyrosine Cysteine C 3
Stop
Leucine
A
Stop
Serine
Leucine Serine Stop Tryptophan G
Leucine Proline Histidine Arginine U
C Leucine Proline Histidine Arginine C
Proline
A
Glutamine
Leucine
Arginine
Leucine Proline Glutamine Arginine G
Isoleucine Threonine Asparagine Serine U
A Isoleucine Threonine Asparagine Serine C
Threonine
A
Isoleucine
Lysine
Arginine
Methionine Threonine Lysine Arginine G
Valine Alanine Aspartic acid Glycine U
G Valine Alanine Aspartic acid Glycine C
A
Glutamic acid
Valine
Glycine
Alanine
Valine Alanine Glutamic acid Glycine G
U U C
© Copyright NewPath Learning www.newpathlearning.com 13