Page 19 - Meiosis_FULL
P. 19
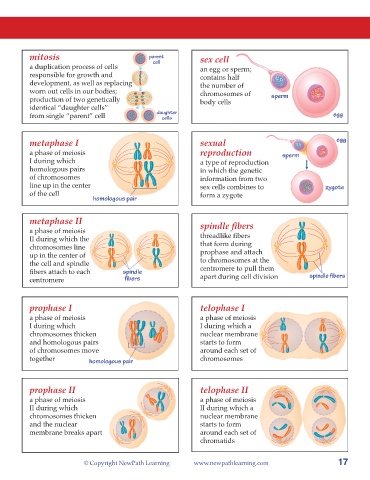
parent ent
mitosis par
cell
cell sex cell
a duplication process of cells an egg or sperm;
responsible for growth and contains half
development, as well as replacing the number of
worn out cells in our bodies; chromosomes of sperm
production of two genetically body cells
identical “daughter cells”
daughter egg
from single “parent” cell daughter
cells
cells
egg
metaphase I sexual
a phase of meiosis reproduction sperm
I during which a type of reproduction
homologous pairs in which the genetic
of chromosomes information from two
line up in the center sex cells combines to zygote
of the cell form a zygote
homologous pair
metaphase II
a phase of meiosis spindle fibers
II during which the threadlike fibers
chromosomes line that form during
up in the center of prophase and attach
the cell and spindle to chromosomes at the
fibers attach to each spindle centromere to pull them spindle fibers
centromere fibers apart during cell division
prophase I telophase I
a phase of meiosis a phase of meiosis
I during which I during which a
chromosomes thicken nuclear membrane
and homologous pairs starts to form
of chromosomes move around each set of
together homologous pair chromosomes
prophase II telophase II
a phase of meiosis a phase of meiosis
II during which II during which a
chromosomes thicken nuclear membrane
and the nuclear starts to form
membrane breaks apart around each set of
chromatids
© Copyright NewPath Learning www.newpathlearning.com 17