Page 109 - Genetics_From_Genes_to_Genomes_6th_FULL_Part2
P. 109
268 Chapter 7 Anatomy and Function of a Gene: Dissection Through Mutation
f. transfusion of plasma from a hemophilia A patient 47. Adult hemoglobin is a multimeric protein with four
into a different hemophilia A patient polypeptides, two of which are α-globin and two of
g. injection of purified vWF into a vWD patient which are β-globin.
h. injection of purified vWF into a hemophilia A a. How many genes are needed to define the structure
patient of the hemoglobin protein?
i. injection of purified factor VIII into a vWD patient b. If a person is heterozygous for wild-type alleles
j. injection of purified factor VIII into a hemophilia and alleles that would yield amino acid substitution
variants for both α-globin and β-globin, how many
A patient different kinds of hemoglobin protein would be
46. Antibodies were made that recognize six proteins that found in the person’s red blood cells and in what
are part of a complex inside the Caenorhabditis elegans proportion? Assume all alleles are expressed at the
one-cell embryo. The mother produces proteins that same level.
are believed to assemble stepwise into a structure in 48. Each complementation group (ARG-E, ARG-F,
the egg, beginning at the embryo’s inner surface. The ARG-G, and ARG-H) in Fig. 7.27b can grow on a
antibodies were used to detect the protein location in unique subset of supplements. Why were these four
embryos produced by mutant mothers [who are ho- subsets the only ones observed? For example, why
mozygous recessive for the gene(s) encoding each were no complementation groups observed that be-
protein]. The C. elegans mothers are self-fertilizing haved like the four hypothetical ones shown in the
hermaphrodites, so no wild-type copy of a gene will following table? (Symbols as in Fig. 7.27b: + means
be introduced during fertilization.
In the following table, * means the protein was growth, − means no growth.)
present and at the embryo surface, − means that the Supplements
protein was not present, and + means that the protein Hypothetical Arginino-
was present but not at the embryo surface. Assume all mutant strain Nothing Ornithine Citrulline succinate Arginine
mutations prevent production of the corresponding Wildtype: Arg + + + + + +
protein. ARG-I − − + − + +
ARG-J − − − + − +
Mutant ARG-K − − + − − +
in gene ARG-L − − + + − +
for Protein production and location
protein A B C D E F
A − + * + * + Section 7.6
B * − * * * *
C * + − + * + 49. In addition to the predominant adult hemoglobin,
D * + * − * + HbA, which contains two α-globin chains and two
E + + + + − + β-globin chains (α 2 β 2 ), there is a minor hemoglobin,
F * + * * * − HbA 2 , composed of two α and two δ chains (α 2 δ 2 ).
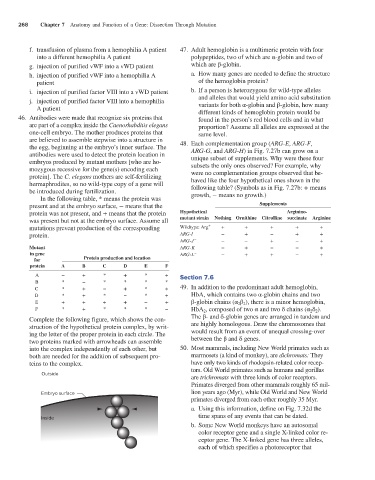
Complete the following figure, which shows the con- The β- and δ-globin genes are arranged in tandem and
struction of the hypothetical protein complex, by writ- are highly homologous. Draw the chromosomes that
ing the letter of the proper protein in each circle. The would result from an event of unequal crossing-over
two proteins marked with arrowheads can assemble between the β and δ genes.
into the complex independently of each other, but 50. Most mammals, including New World primates such as
both are needed for the addition of subsequent pro- marmosets (a kind of monkey), are dichromats: They
teins to the complex. have only two kinds of rhodopsin-related color recep-
tors. Old World primates such as humans and gorillas
Outside
are trichromats with three kinds of color receptors.
Primates diverged from other mammals roughly 65 mil-
Embryo surface lion years ago (Myr), while Old World and New World
primates diverged from each other roughly 35 Myr.
a. Using this information, define on Fig. 7.32d the
time spans of any events that can be dated.
Inside
b. Some New World monkeys have an autosomal
color receptor gene and a single X-linked color re-
ceptor gene. The X-linked gene has three alleles,
each of which specifies a photoreceptor that